GeaFlow介绍
GeaFlow(品牌名TuGraph-Analytics)是蚂蚁集团开源的分布式实时图计算引擎,目前广泛应用于金融风控、社交网络、知识图谱以及数据应用等场景。GeaFlow的核心能力是流式图计算,流式图计算相比离线图计算提供了一种高时效性低延迟的图计算模式,更多详细内容参考GeaFlow GitHub介绍(https://github.com/TuGraph-family/tugraph-analytics).
GeaFlow整体架构如下所示:

- GeaFlow DSL GeaFlow对用户提供图表融合分析语言,采用SQL + ISO/GQL方式.用户可以通过类似SQL编程的方式编写实时图计算任务.
- GraphView API GeaFlow以GraphView为核心定义的一套图计算的编程接口,包含图构建、图计算以及Stream API接口.
- GeaFlow Runtime GeaFlow运行时,包含GeaFlow图表算子、task调度、failover以及shuffle等核心功能.
- GeaFlow State GeaFlow的图状态存储,用于存储图的点边数据.同时流式计算的状态如聚合状态也存放在State中.
- K8S Deployment GeaFlow支持K8S的方式进行部署运行.
- GeaFlow Console GeaFlow的管控平台,包含作业管理、元数据管理等功能.
PageRank算法介绍
PageRank是图计算领域一个应用广泛的算法,由Google公司创始人之一拉里·佩奇与谢尔盖·布林在1998年发明,主要用于网页的排序。该算法基于网页之间相互引用的关系,将网页评分的思想引入到搜索引擎中,用于计算网页的重要度和排名。
PageRank算法的核心思想是:一个网页的重要度是由其他网页对它的引用数量和质量决定的。如果一个网页被其他网页引用得多,那么它的重要度就越高。同时,如果一个网页的引用来源也很重要,那么它对被引用网页的贡献也会更大。
实现PageRank算法的具体步骤包括:首先构建网页之间的链接关系图,然后对图进行迭代计算,直到收敛为止。在每一次迭代中,每个网页的得分都会被重新计算,并更新到下一次迭代中。最后,按照网页得分的大小对搜索结果进行排序,输出排名前几位的网页。如下有4个页面,A, B, C, D:
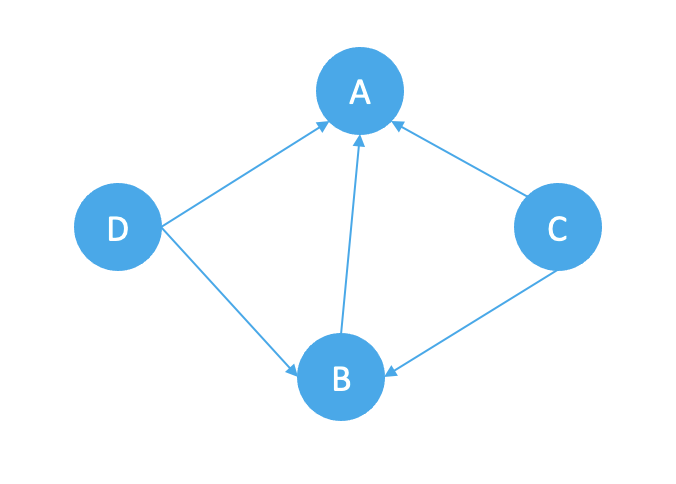
以A点为例,其每一轮的PageRank值计算方法如下:
PR(A) = d * (PR(D)/ 2 + PR(B)/1 + PR(C)/2) + (1- d)
每一个点的PageRank值等于其入点的PageRank值除以入点出边数的加权和, 其中d为0~1之间的修正系数.
PageRank算法在搜索引擎中广泛应用,成为搜索引擎排名的重要算法之一。除此之外,PageRank算法的思想也在社交网络、推荐系统等领域得到了应用。
TuGraph-Analytics实现PageRank
接口与实现
TuGraph-Analytics支持在图查询里调用图算法,语法形式如下:
INSERT INTO tbl_result
CALL page_rank() YIELD (vid, prValue)
RETURN vid, prValue;我们通过CALL语句调用具体的算法,通过YIELD定义算法的返回字段,比如page_rank算法返回点id和page rank值两个字段,则可以通过YIELD(vid, prValue)来表示。
DSL里面实现一个图算法需要实现AlgorithmUserFunction接口,其定义如下:
/** * Interface for the User Defined Graph Algorithm. * @param <K> The id type for vertex. * @param <M> The message type for message send between vertices. */ public interface AlgorithmUserFunction<K, M> extends Serializable {/** * Init method for the function * @param context The runtime context. * @param params The parameters for the function. */ void init(AlgorithmRuntimeContext<K, M> context, Object[] params); /** * Processing method for each vertex and the messages it received. */ void process(RowVertex vertex, Iterator<M> messages); /** * Returns the output type for the function. */ StructType getOutputType();
}
- init
算法的初始化接口,主要完成算法的一些初始化操作. PageRank的init方法实现如下:
@Override
public void init(AlgorithmRuntimeContext context, Object[] parameters) {
this.context = context;
if (parameters.length > 3) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Only support zero or more arguments, false arguments "
+ "usage: func([alpha, [convergence, [max_iteration]]])");
}
// 修正系数,即前面介绍的参数d.
if (parameters.length > 0) {
alpha = Double.parseDouble(String.valueOf(parameters[0]));
}
// PR值更新阀值,当点的pr差值小于该值时,不再更新pr值.
if (parameters.length > 1) {
convergence = Double.parseDouble(String.valueOf(parameters[1]));
}
// 迭代次数
if (parameters.length > 2) {
iteration = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(parameters[2]));
}
}- process
算法的主要处理逻辑,入参为当前Active点和要处理的消息,PageRank主要实现如下:
@Override
public void process(RowVertex vertex, Iterator messages) {
....if (context.getCurrentIterationId() == 1L) { // 首轮迭代设置pr初始值,并发送给出边,同时更新当前点的pr值。 double initValue = 1.0; sendMessageToNeighbors(outEdges, initValue / outEdges.size()); ... context.updateVertexValue(ObjectRow.create(initValue)); } else if (context.getCurrentIterationId() < iteration) { double sum = 0.0; while (messages.hasNext()) { double input = (double) messages.next(); input = input > 0 ? input : 0.0; sum += input; } // 计算当前迭代的pr值 double pr = (1 - alpha) + (sum * alpha); double currentPr = (double) vertex.getValue().getField(0, DoubleType.INSTANCE); if (Math.abs(currentPr - pr) > convergence) { // pr值发送给出边目标点. sendMessageToNeighbors(outEdges, pr / outEdges.size()); } context.updateVertexValue(ObjectRow.create(pr)); } else { // 到达最大迭代次数,结束本轮迭代,take最终计算结果. double currentPr = (double) vertex.getValue().getField(0, DoubleType.INSTANCE); context.take(ObjectRow.create(vertex.getId(), currentPr)); return; } }</code></pre></div></div><ul class="ul-level-0"><li>getOutputType</li></ul><p>定义算法返回类型,PageRank实现如下:</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>java</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-java"><code class="language-java" style="margin-left:0"> @Override public StructType getOutputType() { return new StructType( // id new TableField("id", LongType.INSTANCE, false), // pr值 new TableField("pr", DoubleType.INSTANCE, false) ); }</code></pre></div></div><h4 id="3t7m0" name="%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E6%B3%A8%E5%86%8C">算法注册</h4><p>算法实现通过注解来定义算法名称,如下所示:</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>java</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-java"><code class="language-java" style="margin-left:0">@Description(name = "page_rank", description = "built-in udga for PageRank")
public class PageRank implements AlgorithmUserFunction {
}
算法和UDF一样,需要注册或者创建后才能使用. DSL内置算法或者UDF在BuildInSqlFunctionTable中进行注册.对于非内置算法,可以通过create function语句来创建.
Create funciton page_rank as 'com.antgroup.geaflow.dsl.udf.graph.PageRank';总结
本文主要介绍实时图计算引擎GeaFlow的基本架构,然后介绍了图算法PageRank的基本原理以及在GeaFlow中的实现细节和使用方式.
GeaFlow(品牌名TuGraph-Analytics) 已正式开源,欢迎大家关注!!!
欢迎给我们 Star 哦!
Welcome to give us a Star!
GitHub👉https://github.com/TuGraph-family/tugraph-analytics
更多精彩内容,关注我们的博客 https://geaflow.github.io/