标题:HoPE: Horizontal Plane Extractor for Cluttered 3D Scenes
作者:Dong, Zhipeng and Gao, Yi and Zhang, Jinfeng and Yan
●论文摘要

在杂乱的三维场景中提取水平面是许多机器人应用的基本步骤。针对一般平面分割方法在这一问题上的局限性,我们提出了一种新的平面提取的算法,它能够在杂乱的有序点云或者是无序点云数据中高效的提取平面。通过预校准或惯性测量单元获得的传感器方向将源点云转换为参考坐标系,提出了一种改进的区域增长算法与Z轴聚类算法结合,一种基于主成分分析(PCA)的点云聚类和分割的方法。此外,我们还提出了一种最近邻平面匹配(NNPM)策略来保持连续序列中提取平面的稳定性。对真实场景和合成场景的定性和定量评估表明,我们的方法在对有噪声的点云数据的处理的鲁棒性、准确性和效率方面优于几种最新的方法。并且该算法已经在github 开源:https://github.com/DrawZeroPoint/hope
●主要贡献
(1)根据三维点云采集设备定向的角度对点云数据进行变换从而简化水平面提取的过程,提供了快速且稳健的点云聚类和分割以及识别的方法。
(2)以一种合理的方式尽量的减少使用阈值的数量来减少算法的不稳定性,能够在预期的精度和高效的计算时间里达到较好的分割效果。
(3)与点云库PCL以及机器人操作系统(ROS)兼容且开源。
●论文图集
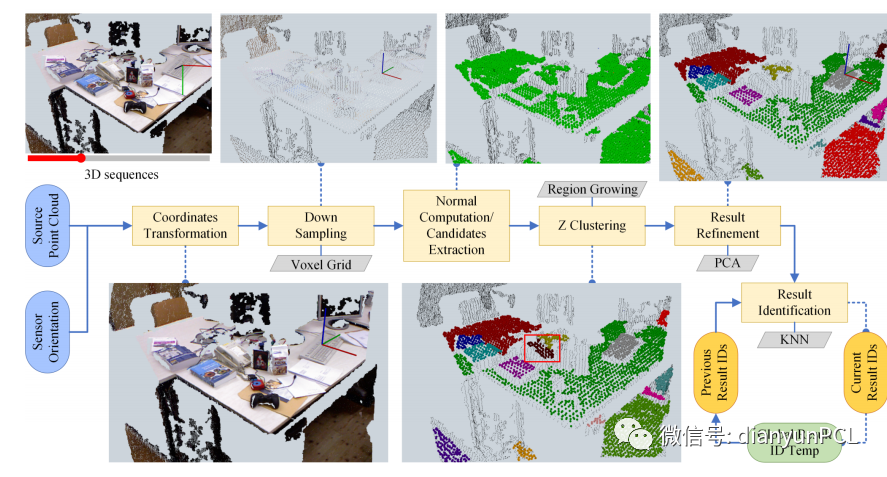
多平面提取的算法流程
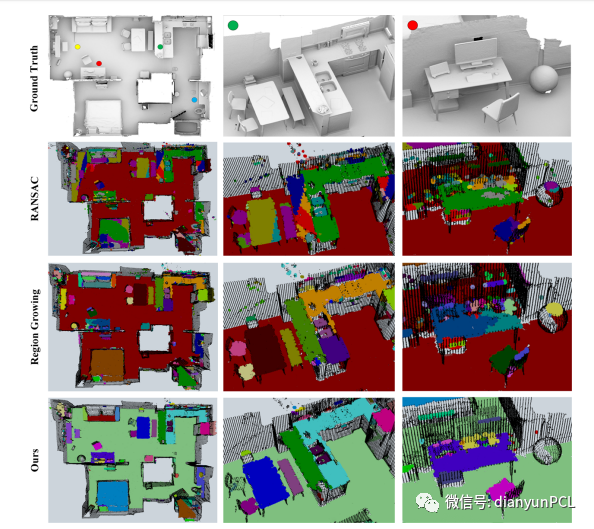
使用RANSAC和区域增长方法与论文中算法的对比截图
文本提出了一个用于从中提取多个水平面的框架,在混乱场景中获得的有组织的和无组织的3D点云。充分利用采集点云数据的方向信息,并简化包括下采样,点云聚类,细化,和结果识别,算法在第一阶段使用了传感器方向的先验知识将源点云转换为参考点云,其z轴指向上方。该算法框架提供了一些专用的且新颖的功能,能够提供稳健且高效的结果。并且框架的潜在优势还在于场景大小的可变性及其对提取的内容进行连续标识的能力。在真实数据集上的实验表明,即便是动态的场景我们的方法可以保持结果的一致性。
●英文摘要

Extracting horizontal planes in heavily cluttered three-dimensional (3D) scenes is an essential procedure for many robotic applications. Aiming at the limitations of general plane segmentation methods on this subject, we present HoPE, a Horizontal Plane Extractor that is able to extract multiple horizontal planes in cluttered scenes with both organized and unorganized 3D point clouds. It transforms the source point cloud in the first stage to the reference coordinate frame using the sensor orientation acquired either by pre-calibration or an inertial measurement unit, thereby leveraging the inner structure of the transformed point cloud to ease the subsequent processes that use two concise thresholds for producing the results. A revised region growing algorithm named Z clustering and a principal component analysis (PCA)-based approach are presented for point clustering and refinement, respectively. Furthermore, we provide a nearest neighbor plane matching (NNPM) strategy to preserve the identities of extracted planes across successive sequences. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations of both real and synthetic scenes demonstrate that our approach outperforms several state-of-the-art methods under challenging circumstances, in terms of robustness to clutter, accuracy, and efficiency. We make our algorithm an off-the-shelf toolbox which is publicly available.