
- 1. 一般Python和numpy实现方式
- 2. 上述两种实现方式比较
- 3. numpy数组
- 4. 创建多维数组
- 5. 选取数组元素
- 6. 数据类型
- 7. 数据类型转换
- 8. 数据类型对象
- 9. 字符编码
- 10. dtype类的属性
- 11. 创建自定义数据类型
- 12. 数组与标量的运算
- 13. 一维数组的索引与切片
- 14. 多维数组的切片与索引
- 15. 布尔型索引
- 16. 花式索引
- 17. 数组转置
- 18. 改变数组的维度
- 19. 组合数组
- 20. 数组的分割
- 21. 数组的属性
- 22. 数组的转换
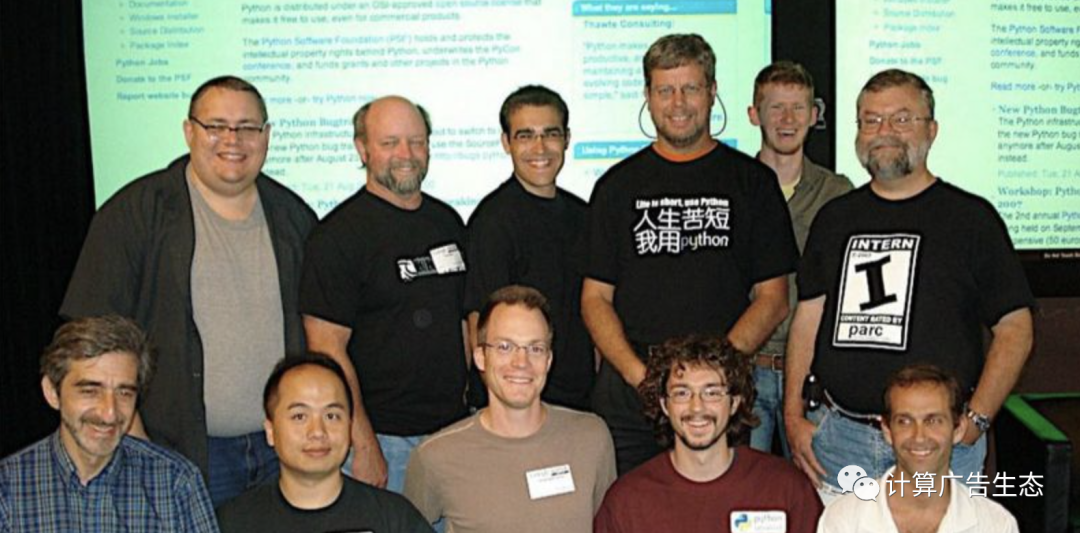
人生苦短我用python!这不是吹牛 ,为什么?咱们大家一起看看心中的大神,其他语言之父们!
Java之父——James Gosling

vb.net之父 ——lan Cooper

PHP之父 ——Rasmus Lerdorf

Go语言之父 ——rob pike

C++之父 ——Bjarne Stroustrupt

最后是重磅的Python之父!

就凭Python在发展接近三十年里,逐渐发展为各行各业的网红语言!
无论是哪个方向工业界 Python 都为其发展带了不可磨灭的功劳!
然后,重磅!今天给大家拿到Python的核心资料!实实在在在工业界会要用到!
公众号后台回复“Python数据科学”全部获取得到!
话不多说,几天先来和大家分享Numpy的基本使用方法,一起学习!
1. 一般Python和numpy实现方式
实现:实现了两个向量的相加
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-此处两种操作方式:
第一种对于每一个元素的操作,第二种是对于整体的操作
向量相加-Python
def pythonsum(n):
a = range(n)
b = range(n)
c = []
for i in range(len(a)):
a[i] = i ** 2
b[i] = i ** 3
c.append(a[i] + b[i])
return c#向量相加-NumPy
import numpy as np
def numpysum(n):
a = np.arange(n) ** 2
b = np.arange(n) ** 3
c = a + b
return c
2. 上述两种实现方式比较
#效率比较
import sys
from datetime import datetime
import numpy as npsize = 1000
start = datetime.now()
c = pythonsum(size)
delta = datetime.now() - start
print "The last 2 elements of the sum", c[-2:]
print "PythonSum elapsed time in microseconds", delta.microseconds
start = datetime.now()
c = numpysum(size)
delta = datetime.now() - start
print "The last 2 elements of the sum", c[-2:]
print "NumPySum elapsed time in microseconds", delta.microseconds
res:
The last 2 elements of the sum [995007996, 998001000] PythonSum elapsed time in microseconds 1110 The last 2 elements of the sum [995007996 998001000] NumPySum elapsed time in microseconds 4052
3. numpy数组
a = arange(5)
a.dtype
a
a.shape
4. 创建多维数组
m = np.array([np.arange(2), np.arange(2)])print m
print m.shape
print m.dtype
np.zeros(10)
np.zeros((3, 6))
np.empty((2, 3, 2))
np.arange(15)
5. 选取数组元素
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])print "In: a"
print aprint "In: a[0,0]"
print a[0,0]print "In: a[0,1]"
print a[0,1]print "In: a[1,0]"
print a[1,0]
print "In: a[1,1]"
print a[1,1]
6. 数据类型
print "In: float64(42)"
print np.float64(42)print "In: int8(42.0)"
print np.int8(42.0)print "In: bool(42)"
print np.bool(42)print np.bool(0)
print "In: bool(42.0)"
print np.bool(42.0)print "In: float(True)"
print np.float(True)
print np.float(False)print "In: arange(7, dtype=uint16)"
print np.arange(7, dtype=np.uint16)print "In: int(42.0 + 1.j)"
try:
print np.int(42.0 + 1.j)
except TypeError:
print "TypeError"
#Type error
print "In: float(42.0 + 1.j)"
print float(42.0 + 1.j)
#Type error
7. 数据类型转换
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
arr.dtype
float_arr = arr.astype(np.float64)
float_arr.dtypearr = np.array([3.7, -1.2, -2.6, 0.5, 12.9, 10.1])
arr
arr.astype(np.int32)
numeric_strings = np.array(['1.25', '-9.6', '42'], dtype=np.string_)
numeric_strings.astype(float)
8. 数据类型对象
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])print a.dtype.byteorder
print a.dtype.itemsize
9. 字符编码
print np.arange(7, dtype='f')
print np.arange(7, dtype='D')print np.dtype(float)
print np.dtype('f')
print np.dtype('d')
print np.dtype('f8')
print np.dtype('Float64')
10. dtype类的属性
t = np.dtype('Float64')
print t.char
print t.type
print t.str
<---------------------------------------------
d
<type 'numpy.float64'>
<f8
11. 创建自定义数据类型
t = np.dtype([('name', np.str_, 40), ('numitems', np.int32), ('price', np.float32)])
print tprint t['name']
itemz = np.array([('Meaning of life DVD', 42, 3.14), ('Butter', 13, 2.72)], dtype=t)
print itemz[1]
<---------------------------------------------
[('name', 'S40'), ('numitems', '<i4'), ('price', '<f4')]
|S40
('Butter', 13, 2.72)
12. 数组与标量的运算
arr = np.array([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]])
arr
arr * arr
arr - arr
1 / arr
arr ** 0.5
<---------------------------------------------
array([[1. , 1.41421356, 1.73205081],
[2. , 2.23606798, 2.44948974]])
13. 一维数组的索引与切片
a = np.arange(9)
print a
print a[3:7]print a[:7:2]
print a[::-1]
s = slice(3,7,2)
print a[s]
s = slice(None, None, -1)
print a[s]
<----------------------------------------
a: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
a[3:7]: [3 4 5 6]
a[:7:2]: [0 2 4 6]
a[::-1]: [8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0]
a[s]: [3 5]
a[s]: [8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0]
14. 多维数组的切片与索引
b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4)print b.shape
print b
print b[0,0,0]
print b[:,0,0]
print b[0]
print b[0, :, :]
print b[0, ...]
print b[0,1]
print b[0,1,::2]
print b[...,1]
print b[:,1]
print b[0,:,1]
print b[0,:,-1]
print b[0,::-1, -1]
print b[0,::2,-1]
print b[::-1]s = slice(None, None, -1)
print b[(s, s, s)]
<-----------------------------------------------
b.shape:
(2, 3, 4)b:
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]][[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]]]b[0,0,0]:
0b[:,0,0]:
[ 0 12]b[0]:
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]b[0, :, :]:
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]b[0, ...]:
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]b[0,1]:
[4 5 6 7]b[0,1,::2]:
[4 6]b[...,1]:
[[ 1 5 9]
[13 17 21]]b[:,1]:
[[ 4 5 6 7]
[16 17 18 19]]b[0,:,1]:
[1 5 9]b[0,:,-1]:
[ 3 7 11]b[0,::-1, -1]:
[11 7 3]b[0,::2,-1]:
[ 3 11]b[::-1]:
[[[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]][[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]]b[(s, s, s)]:
[[[23 22 21 20]
[19 18 17 16]
[15 14 13 12]]
[[11 10 9 8]
[ 7 6 5 4]
[ 3 2 1 0]]]
15. 布尔型索引
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe'])
data = randn(7, 4)
names
datanames == 'Bob'
data[names == 'Bob']data[names == 'Bob', 2:]
data[names == 'Bob', 3]names != 'Bob'
data[-(names == 'Bob')]mask = (names == 'Bob') | (names == 'Will')
mask
data[mask]data[data < 0] = 0
datadata[names != 'Joe'] = 7
data
<--------------------------------------------------
['Bob' 'Joe' 'Will' 'Bob' 'Will' 'Joe' 'Joe']
[[ 1.43829891 -1.83591387 0.63309836 -0.0836829 ]
[ 0.26632654 -0.22359825 0.27609837 0.37220043]
[ 0.98970563 0.31626285 0.80613492 -2.52762618]
[-0.95268723 0.55888808 -0.37982142 -0.79270072]
[ 0.00445215 -0.55879136 0.41136902 -0.3590782 ]
[-0.49665784 -0.09281634 0.65459855 1.35881415]
[ 0.21105429 -0.99353232 1.29098127 -1.25913777]]
[ True False True True True False False]
[[ 1.43829891 -1.83591387 0.63309836 -0.0836829 ]
[ 0.98970563 0.31626285 0.80613492 -2.52762618]
[-0.95268723 0.55888808 -0.37982142 -0.79270072]
[ 0.00445215 -0.55879136 0.41136902 -0.3590782 ]]
[[1.43829891 0. 0.63309836 0. ]
[0.26632654 0. 0.27609837 0.37220043]
[0.98970563 0.31626285 0.80613492 0. ]
[0. 0.55888808 0. 0. ]
[0.00445215 0. 0.41136902 0. ]
[0. 0. 0.65459855 1.35881415]
[0.21105429 0. 1.29098127 0. ]]
[[7. 7. 7. 7. ]
[0.26632654 0. 0.27609837 0.37220043]
[7. 7. 7. 7. ]
[7. 7. 7. 7. ]
[7. 7. 7. 7. ]
[0. 0. 0.65459855 1.35881415]
[0.21105429 0. 1.29098127 0. ]]
16. 花式索引
arr = np.empty((8, 4))
for i in range(8):
arr[i] = i
arrarr[[4, 3, 0, 6]]
arr[[-3, -5, -7]]
arr = np.arange(32).reshape((8, 4))
arr
arr[[1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2]]arr[[1, 5, 7, 2]][:, [0, 3, 1, 2]]
arr[np.ix_([1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2])]
<---------------------------------------------
arr = np.empty((8, 4))
print arr
array([[-3.10503618e+231, -3.10503618e+231, 3.32457344e-309,2.14057207e-314],
[-3.10503618e+231, -3.10503618e+231, 2.14038712e-314,1.27319747e-313],
[ 1.27319747e-313, 1.27319747e-313, 2.12199579e-314,1.91163808e-313],
[ 2.14059464e-314, 2.12199580e-314, 3.18573536e-313,2.14059516e-314],
[ 2.12199580e-314, 1.25160619e-308, 0.00000000e+000,0.00000000e+000],
[ 0.00000000e+000, 0.00000000e+000, 0.00000000e+000,0.00000000e+000],
[ 0.00000000e+000, 0.00000000e+000, 0.00000000e+000,0.00000000e+000],
[ 0.00000000e+000, 0.00000000e+000, 2.12199579e-314,2.14062641e-314]])for i in range(8):
arr[i] = i
print arr
[[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 1. 1. 1.]
[2. 2. 2. 2.]
[3. 3. 3. 3.]
[4. 4. 4. 4.]
[5. 5. 5. 5.]
[6. 6. 6. 6.]
[7. 7. 7. 7.]]同时选取多行,甚至多列,换位
print arr[[4, 3, 0, 6]] ### 注意与arr[4]的不同
[[4. 4. 4. 4.]
[3. 3. 3. 3.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[6. 6. 6. 6.]]print arr[[-3, -5, -7]] ### 注意与arr[4]的不同
[[5. 5. 5. 5.]
[3. 3. 3. 3.]
[1. 1. 1. 1.]]arr = np.arange(32).reshape((8, 4))
print arr
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]
[24 25 26 27]
[28 29 30 31]]
print arr[[1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2]]
[ 4 23 29 10]print arr[[1, 5, 7, 2]][:, [0, 3, 1, 2]]
[[ 4 7 5 6]
[20 23 21 22]
[28 31 29 30]
[ 8 11 9 10]]
print arr[np.ix_([1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2])]
[[ 4 7 5 6]
[20 23 21 22]
[28 31 29 30]
[ 8 11 9 10]]
17. 数组转置
arr = np.arange(15).reshape((3, 5))
arr
arr.T
<--------------------------------------
array([[ 0, 5, 10],
[ 1, 6, 11],
[ 2, 7, 12],
[ 3, 8, 13],
[ 4, 9, 14]])
18. 改变数组的维度
b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4) ## 与resize()的区别,resize会改变print b
print b.ravel()
print b.flatten()
b.shape = (6,4)
print b
print b.transpose() # 转置
b.resize((2,12)) ## 和reshape()一样,resize会改变原数据
print b
numpy中的ravel()、flatten()、squeeze()都有将多维数组转换为一维数组的功能,区别:
ravel():如果没有必要,不会产生源数据的副本
flatten():返回源数据的副本
squeeze():只能对维数为1的维度降维
19. 组合数组
a = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3)print a
b = 2 * a
print b
print np.hstack((a, b))
print np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1)
print np.vstack((a, b))
print np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0)
print np.dstack((a, b)) # 深度合并
oned = np.arange(2)
#-------------另外一种实现--------------------
print onedtwice_oned = 2 * oned
print twice_oned
print np.column_stack((oned, twice_oned))
print np.column_stack((a, b))
print np.column_stack((a, b)) == np.hstack((a, b))
print np.row_stack((oned, twice_oned))
print np.row_stack((a, b))
print np.row_stack((a,b)) == np.vstack((a, b))
20. 数组的分割
a = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)
print a
print np.hsplit(a, 3)
print np.split(a, 3, axis=1)
<----------------------------------------------------
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]][
array([[0],[3],[6]]),
array([[1],[4],[7]]),
array([[2],[5],[8]])
][
array([[0],[3],[6]]),
array([[1],[4],[7]]),
array([[2],[5],[8]])
]print np.vsplit(a, 3)
print np.split(a, 3, axis=0)
c = np.arange(27).reshape(3, 3, 3)
print c
print np.dsplit(c, 3)
<------------------------------------------------
[array([[0, 1, 2]]), array([[3, 4, 5]]), array([[6, 7, 8]])]
[array([[0, 1, 2]]), array([[3, 4, 5]]), array([[6, 7, 8]])]
[[[ 0 1 2]
[ 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8]][[ 9 10 11]
[12 13 14]
[15 16 17]][[18 19 20]
[21 22 23]
[24 25 26]]]
[array([[[ 0],
[ 3],
[ 6]],[[ 9], [12], [15]], [[18], [21], [24]]]), array([[[ 1], [ 4], [ 7]], [[10], [13], [16]], [[19], [22], [25]]]), array([[[ 2], [ 5], [ 8]], [[11], [14], [17]], [[20], [23], [26]]])]
21. 数组的属性
b=np.arange(24).reshape(2,12)
print b.ndim
print b.size
print b.itemsize
print b.nbytesb = np.array([ 1.+1.j, 3.+2.j])
print b.real
print b.imag
b=np.arange(4).reshape(2,2)
print b.flat
print b.flat[2]
<--------------------------------------------
2
24
8
192
[1. 3.]
[1. 2.]
<numpy.flatiter object at 0x7fdb1d4eae00>
2
22. 数组的转换
b = np.array([ 1.+1.j, 3.+2.j])
print bprint b.tolist()
print b.tostring()
print np.fromstring('\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xf0?\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xf0?\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x08@\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00@', dtype=complex)
print np.fromstring('20:42:52',sep=':', dtype=int)
print b
print b.astype(int)
print b.astype('complex')
作者:Johngo
配图:Pexels