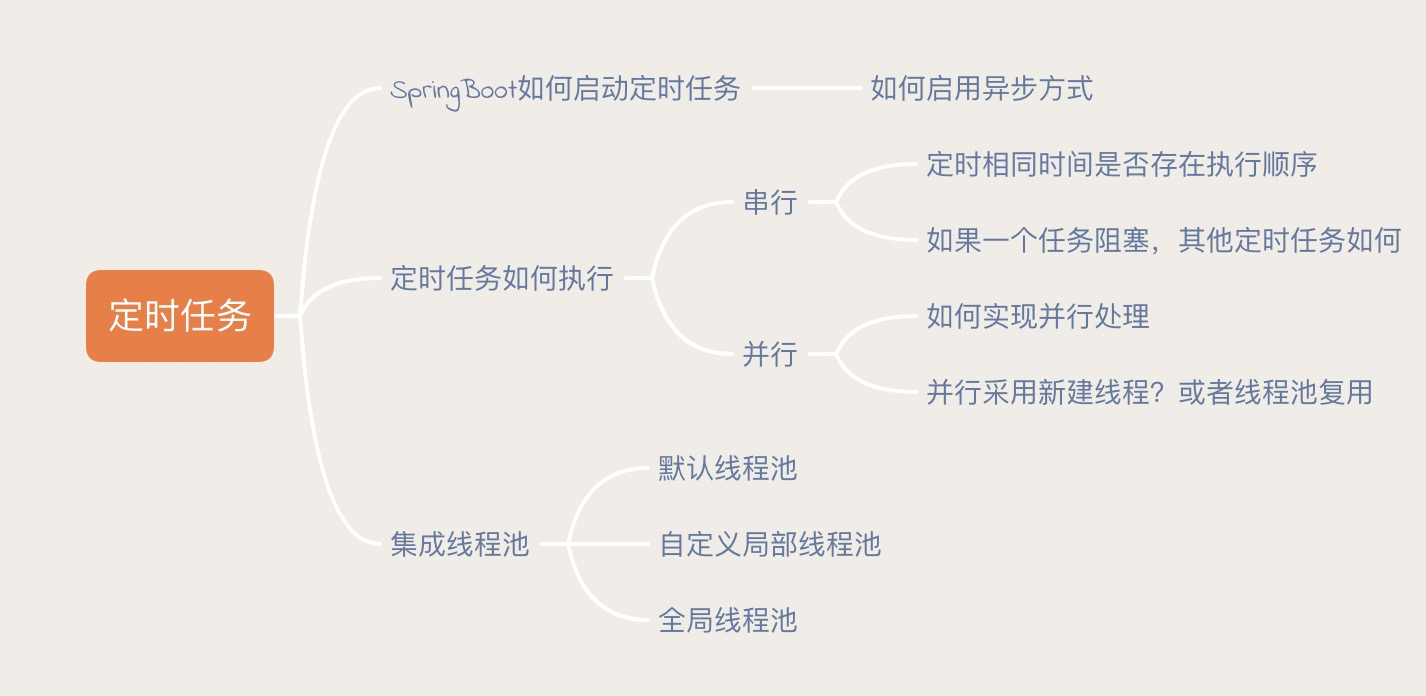
项目中最近使用了多个定时任务处理业务需求,于是在实现业务逻辑过程中,产生了上图一些思考和疑问,现在利用空余时间进行一次复盘。
项目搭建
- 项目搭建环境:JDK1.8+SpringBoot@Component
public class ScheduledTask {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?") public void scheduledTask1() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask1 " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } @Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?") public void scheduledTask2() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask2 " + System.currentTimeMillis()); }}
- 主启动类:加上
@EnableScheduling - 新建定时任务配置类:
ScheduledTask;定义两个定时任务,简单打印一下线程名字和时间戳
源码如下:
一、多任务串行执行
- 相同定时任务
先解决多任务定时相同时间,是否存在优先级执行顺序,执行上面的代码,打印日志如下图:
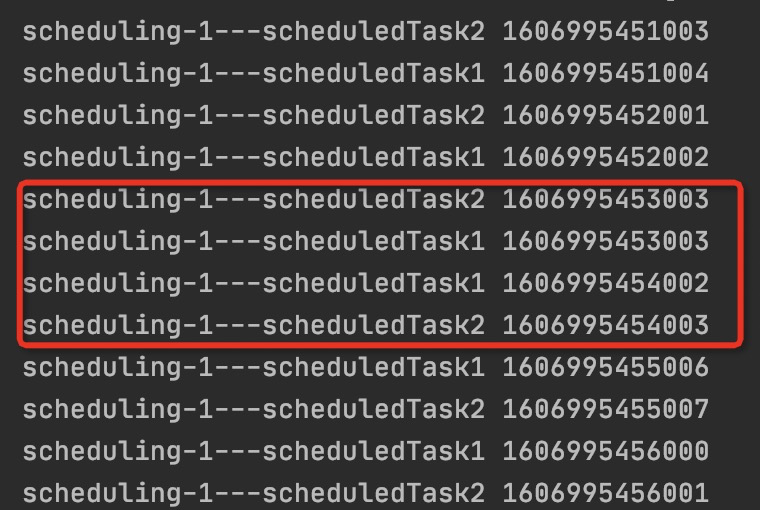
从控制台日志发现,两个定时任务并没有存在一定的执行顺序,存在乱序现象。
故:串行定时任务,没有明显的优先级关系。
- 一个定时任务阻塞
为了实现此场景的条件,将定时任务1中添加死循环逻辑。源码改动如下:
@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?")
public void scheduledTask1() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask1 " + System.currentTimeMillis());
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}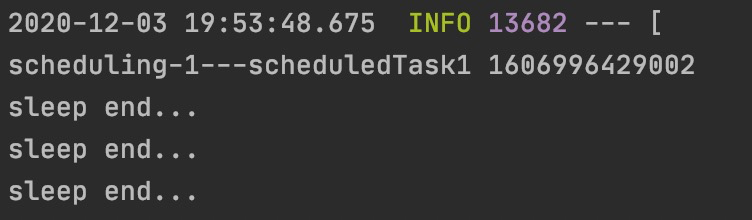
从控制台可以得出:多个定时任务时串行执行的,如果一个任务出现阻塞,其他的任务都会受到影响。
二、多任务并行执行
如果要实现并行执行,启动类需要在上面的基础上新增注解@EnableAsync。任务方法上新增@Async注解。
源码如下:
@Component
public class ScheduledTask {@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?") @Async public void scheduledTask1() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask1 " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } @Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?") @Async public void scheduledTask2() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask2 " + System.currentTimeMillis()); }
}
执行结果如下图:
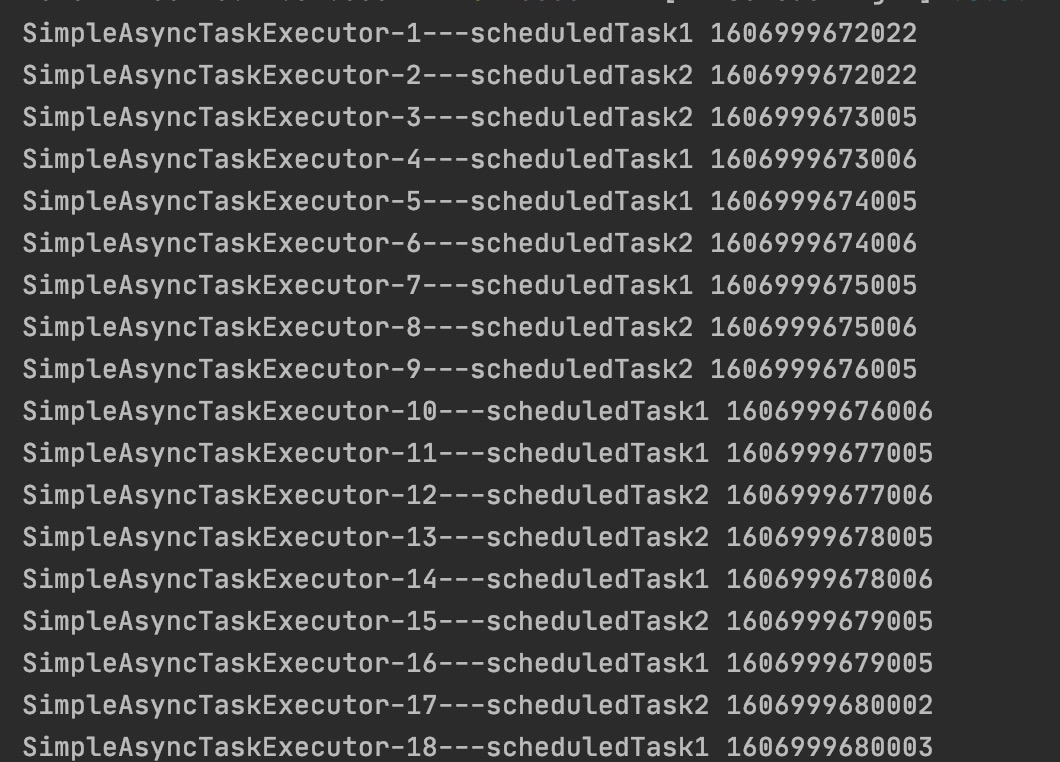
从控制台中打印的线程名发现:每次执行任务时,都是创建新的线程执行,使用默认线程池SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor。
默认情况下异步调用使用的线程池是SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor,该线程池是不被推荐,因为该线程池的线程不重用,每次调用都会创建一个新的线程。所以需要我们自定义线程池。
三、自定义线程池
- 自定义局部线程池
局部线程池实际上就是指异步方法上需要指定使用该线程池,否则将使用默认线程池。
配置异步线程池源码如下:
@Component
public class AsyncTaskExecutorConfig {/** * 重写AsyncTaskExecutor对象,实现全局异步线程,即@Async注解需指定线程池 */
@Bean(value = "asyncTaskExecutor")
public AsyncTaskExecutor asyncTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("defineAsyncTask-");
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setCorePoolSize(3);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
/*
线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略(rejection policy):
当线程池已经达到最大线程数量,没有空闲线程时,新任务该如何处理
可选策略:
CallerRunsPolicy:当线程池没有能力处理时直接在执行方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务
如果执行程序已经关闭,将丢弃该任务.
AbortPolicy:处理程序遭到拒绝时将抛出 RejectedExecutionException
*/
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//等待所有任务调度完成在关闭线程池,保证所有的任务被正确处理
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
//线程池关闭时等待其他任务的时间,不能无限等待,确保应用最后能被关闭。而不是无限期阻塞
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
//线程池初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
定时任务源码修改如下:
@Component
public class ScheduledTask {@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?") //指定自定义线程池 @Async("asyncTaskExecutor") public void scheduledTask1() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask1 " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } @Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?") @Async//未指定线程池,则使用默认线程池 public void scheduledTask2() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---scheduledTask2 " + System.currentTimeMillis()); }
}
控制台执行结果如下:
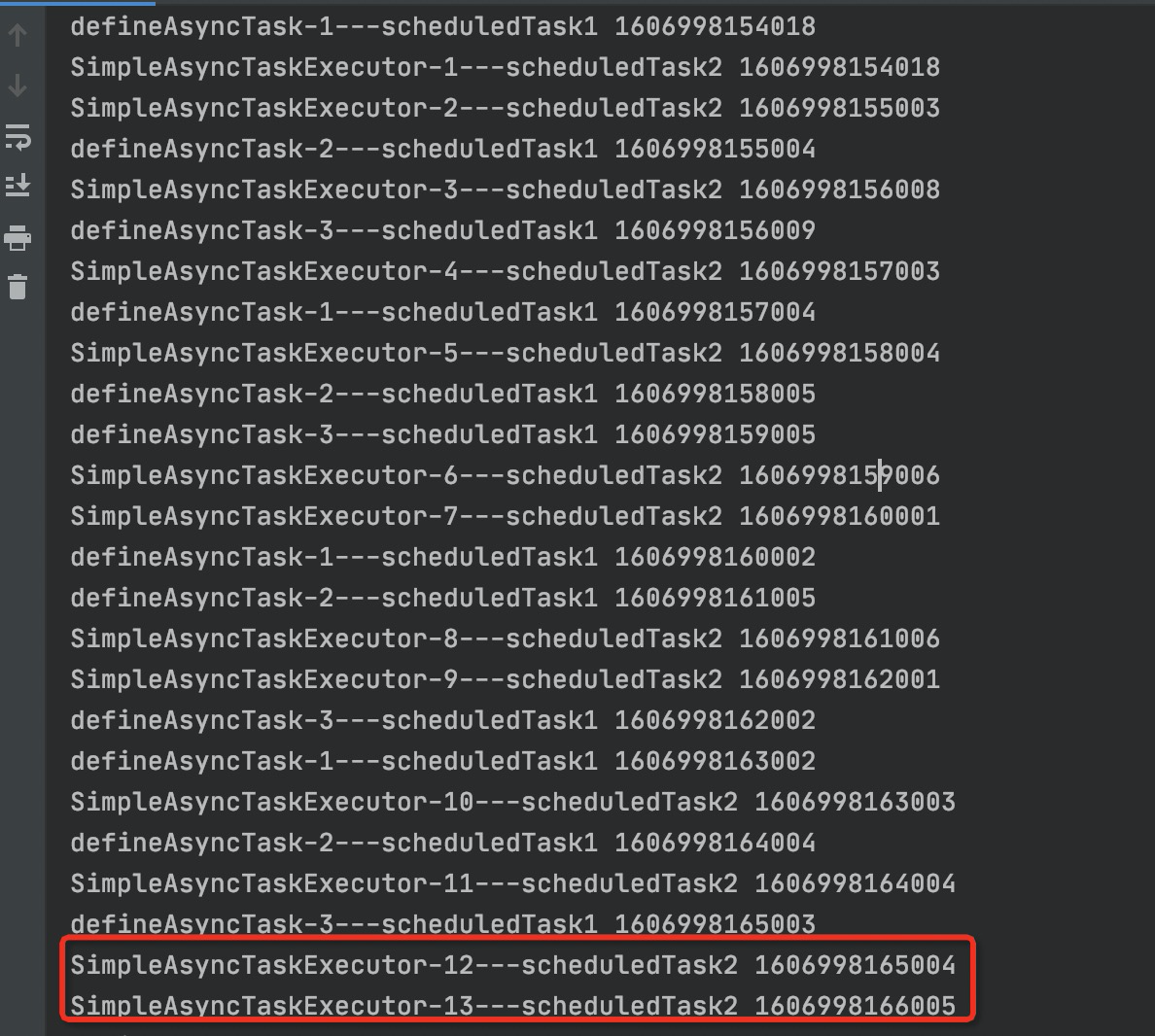
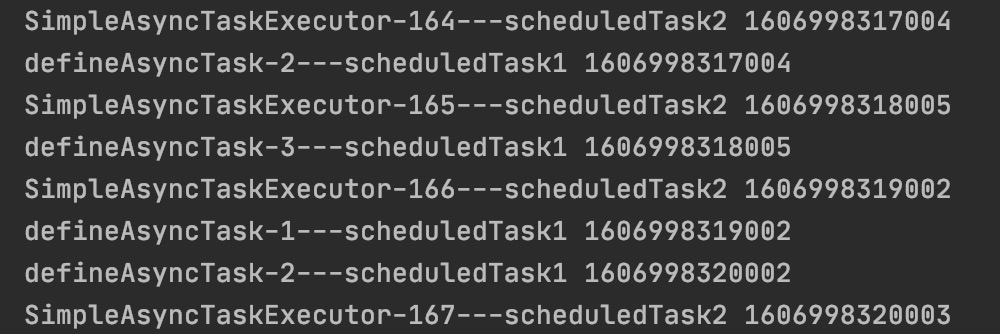
从图中依据线程名字,看到任务1均有自定义线程池defineAsyncTask-*执行,同时验证默认线程池SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor一直创建新线程执行。
- 定义全局线程池
上面需在@Async()注解中指定使用自定义线程池才有效,如果我们即不想指定线程池,又不想使用默认线程池池---全局线程池。
定义全局线程池可以通过实现 AsyncConfigurer 或者继承 AsyncConfigurerSupport。
源码如下:
@Configuration
public class AsyncGlobalConfig extends AsyncConfigurerSupport {
private static final String THREAD_PREFIX = "defineGlobalAsync-";@Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); executor.setThreadNamePrefix(THREAD_PREFIX); executor.setCorePoolSize(3); executor.setMaxPoolSize(10); executor.setQueueCapacity(100); executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60); executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true); executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60); executor.initialize(); return executor; }
}
再次执行上面的任务,结果如下:
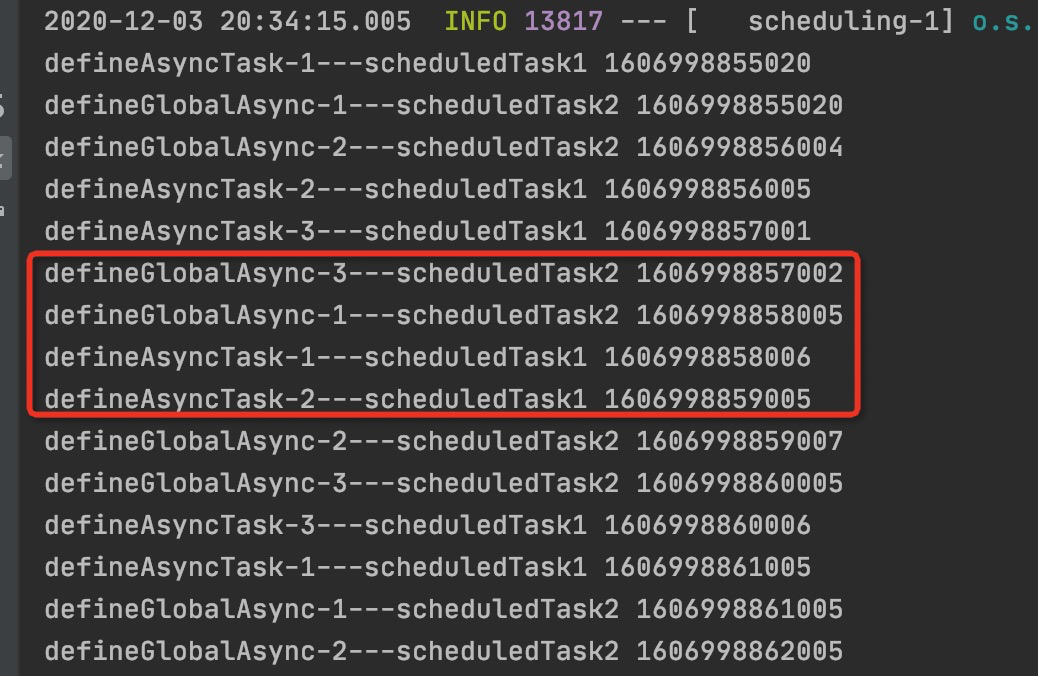
任务1,指定自定义线程池,则有该线程池执行任务,其余未指定线程池,则使用自定义的全局线程池执行任务。
四、异常处理
使用过线程池执行任务的伙伴应该会知道,线程提交任务分为execute()方式和submit()方式。
- 对于异步submit提交任务时,使用Future.get()方法获取返回结果时,主线程阻塞并可以处理线程池中的异常。
- 对于execute()方式提交任务,当异步任务返回类型为 void,异常不会传播到调用线程,故需要通过实现
AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler接口创建自定义异常处理。
故在上面配置全局线程池的基础上,处理异常。从源码中可以得出AsyncConfigurerSupport提供了两个方法,其中getAsyncExecutor()是定义线程池的,getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler()是用于处理异常的。
处理异常源码实现如下:
- 自定义异常处理实现类:
static class CustomAsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable e, Method method, Object... args) {
//处理异常
}
}</code></pre></div></div><ul class="ul-level-0"><li>定义全局线程池重写getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new CustomAsyncExceptionHandler();
}</li></ul>