前言 大家好吖,欢迎来到 YY 滴C++系列 ,热烈欢迎! 本章主要内容面向接触过C++的老铁 主要内容含:
一、string类——基本介绍
- string是表示字符串的字符串类。
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,可以视作在常规接口基础上再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
- string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string;
- 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
二、string类——使用环境准备
- 在使用string类时,必须包含
#include<iostream> #include<string>以及 展开命名空间using namespace std;
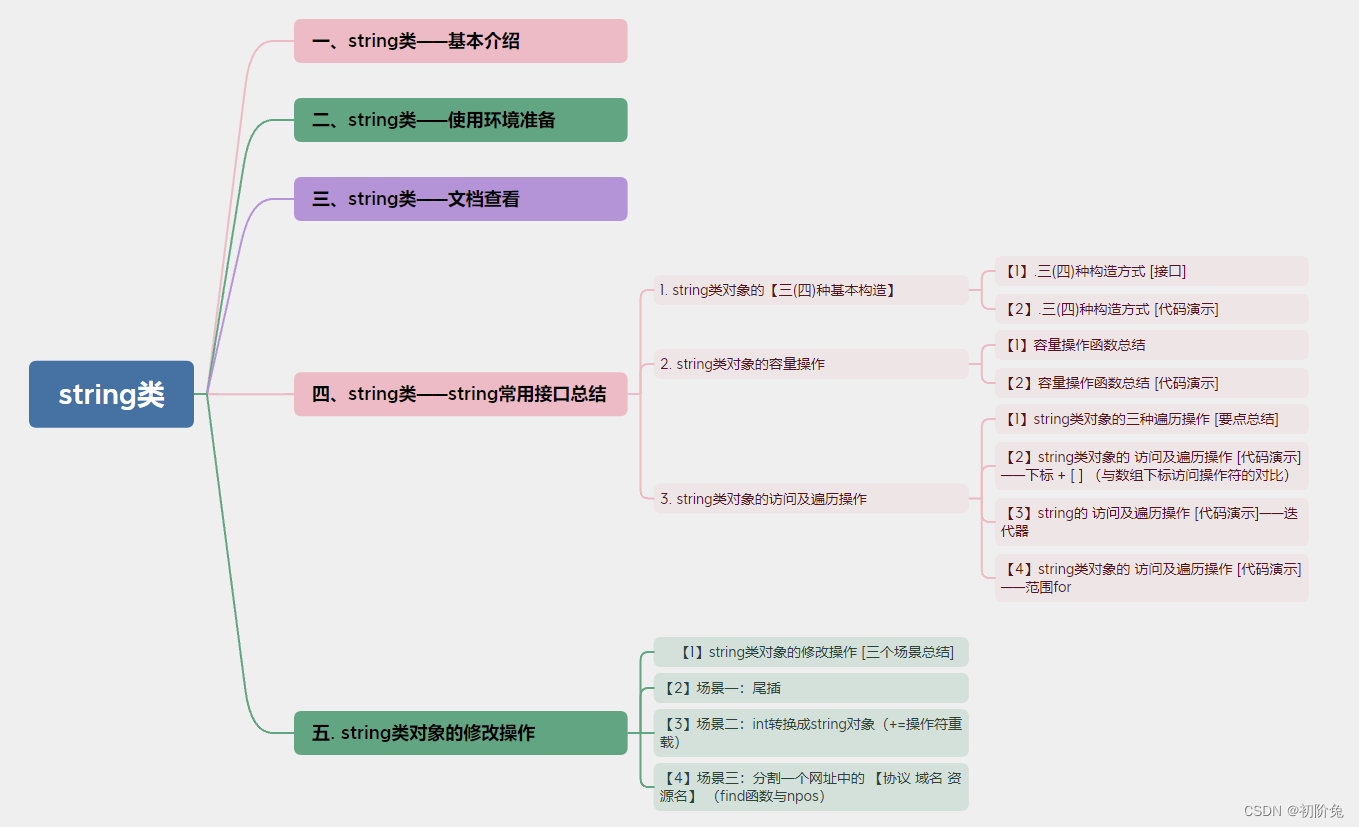
三、string类——文档查看
- 查看所有接口网站:https://cplusplus.com
- PS:string不属于传统的STL容器,它的出现早于STL,所以要在Other中才能找到
四、string类——string常用接口总结
1. string类对象的【三(四)种基本构造】
【1】.三(四)种构造方式 [接口]
构造函数声明 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
string() | 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串 |
string(const char* s) | 用C-string来构造string类对象 |
string(size_t n, char c) | string类对象中包含n个字符c |
string(const string&s) | 拷贝构造函数 |
【2】.三(四)种构造方式 [代码演示]
void Teststring() { string s1; //构造空的string类对象s1string s2("hello bit"); // 用C格式字符串构造string类对象s2
string s4(10, ''); //string类对象中包含10个字符
string s3(s2); // 拷贝构造s3
}
2. string类对象的容量操作
【1】容量操作函数总结
函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
size(重点) | 返回字符串有效字符长度 (与length相同,引入size命名区分,是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size() |
length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
empty (重点) | 检测字符串释放为 空串 ,是 返回true 否则 返回false |
clear (重点) | 清空有效字符(不改变底层空间) |
reserve (重点) | 为字符串预留空间(当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reservr不会改变容量大小) |
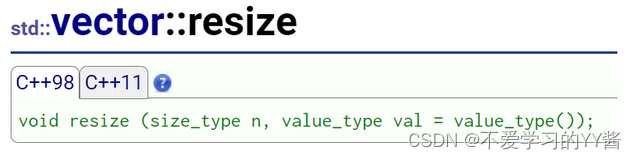
resize (重点) | 将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充(注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变) |
【2】容量操作函数总结 [代码演示]
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;size_t old = s1.capacity(); s.resize(8); s.resize(13, 'x'); return 0;
}
3. string类对象的访问及遍历操作
【1】string类对象的三种遍历操作 [要点总结]
函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
下标 + [ ] | |
operator[] (重点) | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用 |
迭代器 | ( 任何容器都支持迭代器,并且用法是类似) |
begin+ end | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
rbegin + rend | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
范围for |
【2】string类对象的 访问及遍历操作 [代码演示]——下标 + [ ] (与数组下标访问操作符的对比)
与数组下标访问操作符的对比:
- string访问的 [ ] 是操作符重载
- 数组的 [ ] 是 指针移动
//与数组的下标访问符的区别 char s3[] = "hello world"; s3[1]++; // -> *(s3+1);数组指针移动s1[1]++; // s1.operator[](1); 操作符重载,改变ASCALL码</code></pre></div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">int main(){
string s0;
string s1("hello world");
// 遍历string
// 下标+[]for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) { s1[i]++; //改变ASCALL码 } cout << endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) { cout << s1[i] <<" "; //遍历打印 } cout << endl;
}
【3】string的 访问及遍历操作 [代码演示]——迭代器
iterator的使用 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
begin +end(重点) | 获取第一个数据位置的iterator/const_iterator, 获取最后一数据的下一个位置的iterator/const_iterator |
rbegin + rend | 获取最后一个数据位置的reverse_iterator,获取第一个数据前一个位置的reverse_iterat |
- 勉强可以将迭代器理解成为【指针】,该指针指向string中的某个节点。
- 任何容器都支持迭代器,并且用法是类似

string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
// 写
(*it)--;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end()) //理解成迭代器指针从s1.begin()头位置通过while循环一直到不为s1.end()尾位置为止
{
// 读
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;【4】string类对象的 访问及遍历操作 [代码演示]——范围for
- 范围for的底层替换为迭代器
- 可以引入auto关键字省去识别操作
string s1("hello world");
//for (char& ch : s1)
for (auto& ch : s1)
{
ch++;
}
cout << endl;
for (char ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;</code></pre></div></div><h4 id="8ekpt" name="%E4%BA%94.-string%E7%B1%BB%E5%AF%B9%E8%B1%A1%E7%9A%84%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C">五. string类对象的修改操作</h4><h5 id="8veeu" name="%E3%80%901%E3%80%91string%E7%B1%BB%E5%AF%B9%E8%B1%A1%E7%9A%84%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C-%5B%E4%B8%89%E4%B8%AA%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93%5D">【1】string类对象的修改操作 [三个场景总结]</h5><div class="table-wrapper"><table><thead><tr><th style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-header"><p>函数名称</p></div></div></th><th style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-header"><p>功能说明</p></div></div></th></tr></thead><tbody><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>场景一:</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p></p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>push_back</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>在字符串后尾插字符c</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>append</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>在字符串后追加一个字符串</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>场景二:</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p></p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>operator+= (重点)</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>在字符串后追加字符串str</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>c_str(重点)</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>返回C格式字符串</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>场景三:</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p></p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>find + npos(重点)</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置(npos该值表示“字符串的结尾位置” )</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>rfind</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>substr</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将截取的字符返回</p></div></div></td></tr></tbody></table></div><p>!](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f6bc3a09b2774a9c83a51d30c07e0ff6.png)</p><h5 id="1f9v0" name="%E3%80%902%E3%80%91%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%B8%80%EF%BC%9A%E5%B0%BE%E6%8F%92">【2】场景一:尾插</h5><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">//场景1:尾插
string s1("hello");
// 尾插入一个字符
s1.push_back('x');
尾插一个字符串
s1.append("world");
s1 += ' ';
s1 += "world";
cout << s1 << endl;</code></pre></div></div><h5 id="d0lmr" name="%E3%80%903%E3%80%91%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%BA%8C%EF%BC%9Aint%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2%E6%88%90string%E5%AF%B9%E8%B1%A1%EF%BC%88+=%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C%E7%AC%A6%E9%87%8D%E8%BD%BD%EF%BC%89">【3】场景二:int转换成string对象(+=操作符重载)</h5><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">//场景2:int 类型转换成string对象
size_t x = 0;
cin >> x;
string xstr;
while (x)
{
size_t val = x % 10;
xstr += ('0'+val);
x /= 10;
}</code></pre></div></div><h5 id="429lp" name="%E3%80%904%E3%80%91%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%B8%89%EF%BC%9A%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E7%BD%91%E5%9D%80%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84-%E3%80%90%E5%8D%8F%E8%AE%AE-%E5%9F%9F%E5%90%8D-%E8%B5%84%E6%BA%90%E5%90%8D%E3%80%91-%EF%BC%88find%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0%E4%B8%8Enpos%EF%BC%89">【4】场景三:分割一个网址中的 【协议 域名 资源名】 (find函数与npos)</h5><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">//场景3:查找和截取 ————分割一个网址中的 【协议 域名 资源名】
string url = "http://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg";
// http://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg
// 协议:protocol 域名:domain 资源名:uri
string protocol;
string domain;
string uri;
size_t pos1 = url.find("://");//记下pos1的位置
if (pos1 != string::npos) //npos该值表示“字符串的结尾位置”
{
protocol = url.substr(0, pos1);//截取协议
}
cout << protocol << endl;
size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3);
if (pos2 != string::npos)
{
domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));//截取域名
uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1);//截取资源名
}
cout << domain << endl;
cout << uri << endl;</code></pre></div></div>