分析结果
先看看最终由本博客分析后绘制出来的总体流程结构图
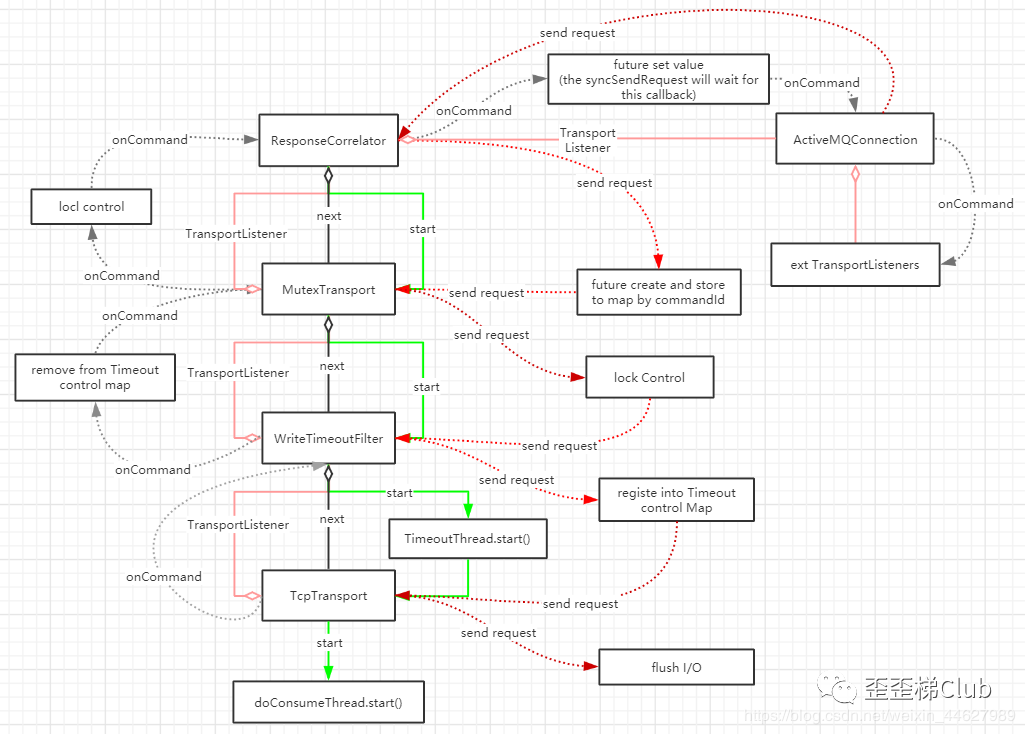
activeMQ流程
创建连接
//1、创建工厂连接对象,需要制定ip和端口号
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://192.168.156.44:61616");
//2、使用连接工厂创建一个连接对象
Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
//3、开启连接
connection.start();
//4、使用连接对象创建会话(session)对象
Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
创建Session时,第一个传入是否开启事务,第二个传入session提交消费消息的方式 接下来看源码处理,生产者id对象由当前sessionID加上使用内部session序列号生成器(long类型自增)生成的id组合构成
public Session createSession(boolean transacted, int acknowledgeMode) throws JMSException { this.checkClosedOrFailed(); this.ensureConnectionInfoSent(); if (!transacted) { if (acknowledgeMode == 0) { throw new JMSException("acknowledgeMode SESSION_TRANSACTED cannot be used for an non-transacted Session"); }if (acknowledgeMode < 0 || acknowledgeMode > 4) { throw new JMSException("...异常信息很长,省略了"); } } return new ActiveMQSession(this, this.getNextSessionId(), transacted ? 0 : acknowledgeMode, this.isDispatchAsync(), this.isAlwaysSessionAsync()); } protected ProducerId getNextProducerId() { return new ProducerId(this.info.getSessionId(), this.producerIdGenerator.getNextSequenceId()); }
最终调用ActiveMQSession的构造方法
new ActiveMQSession(this, this.getNextSessionId(), transacted ? 0 : acknowledgeMode, this.isDispatchAsync(), this.isAlwaysSessionAsync())
也就是说,如果传入了开启事务,使用ack为0的模式创建session,否则使用给进来的ack参数,根据不同ack,使用不同的提交确认策略
AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE = 1 自动确认
CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE = 2 客户端手动确认
DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE = 3 自动批量确认
SESSION_TRANSACTED = 0 事务提交并确认
INDIVIDUAL_ACKNOWLEDGE = 4 单条消息确认
翻阅了session里面无果,决定先从connection和connectionFactory入手,factory中也没开启发送相关的参数,进入connection源码查看
Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
最终会create一个Transport 对象,并调用他的start方法(有内味了),继续
protected ActiveMQConnection createActiveMQConnection(String userName, String password) throws JMSException {
if (this.brokerURL == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("brokerURL not set.");
} else {
ActiveMQConnection connection = null;try { Transport transport = this.createTransport(); connection = this.createActiveMQConnection(transport, this.factoryStats); connection.setUserName(userName); connection.setPassword(password); this.configureConnection(connection); transport.start(); if (this.clientID != null) { connection.setDefaultClientID(this.clientID); } return connection; } catch (JMSException var8) { try { connection.close(); } catch (Throwable var6) { } throw var8; } catch (Exception var9) { try { connection.close(); } catch (Throwable var7) { } throw JMSExceptionSupport.create("Could not connect to broker URL: " + this.brokerURL + ". Reason: " + var9, var9); } } } protected Transport createTransport() throws JMSException { try { URI connectBrokerUL = this.brokerURL; String scheme = this.brokerURL.getScheme(); if (scheme == null) { throw new IOException("Transport not scheme specified: [" + this.brokerURL + "]"); } else { if (scheme.equals("auto")) { connectBrokerUL = new URI(this.brokerURL.toString().replace("auto", "tcp")); } else if (scheme.equals("auto+ssl")) { connectBrokerUL = new URI(this.brokerURL.toString().replace("auto+ssl", "ssl")); } else if (scheme.equals("auto+nio")) { connectBrokerUL = new URI(this.brokerURL.toString().replace("auto+nio", "nio")); } else if (scheme.equals("auto+nio+ssl")) { connectBrokerUL = new URI(this.brokerURL.toString().replace("auto+nio+ssl", "nio+ssl")); } return TransportFactory.connect(connectBrokerUL); } } catch (Exception var3) { throw JMSExceptionSupport.create("Could not create Transport. Reason: " + var3, var3); } }
先根据传进来的broker的url解析成新的url,接着调用TransportFactory.connect(connectBrokerUL),在里面根据url解析得到一个wireFormat对象(主要是对流的字节数据的解析协议,比如有mqtt协议的wireformat,有amqp协议的wireformat),接着使用wireformat和broker的url信息创建一个Transport
Transport包装
public static Transport connect(URI location) throws Exception {
TransportFactory tf = findTransportFactory(location);
return tf.doConnect(location);
}
public Transport doConnect(URI location) throws Exception {
try {
Map<String, String> options = new HashMap(URISupport.parseParameters(location));
if (!options.containsKey("wireFormat.host")) {
options.put("wireFormat.host", location.getHost());
}WireFormat wf = this.createWireFormat(options); Transport transport = this.createTransport(location, wf); Transport rc = this.configure(transport, wf, options); IntrospectionSupport.extractProperties(options, "auto."); if (!options.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid connect parameters: " + options); } else { return rc; } } catch (URISyntaxException var6) { throw IOExceptionSupport.create(var6); } }
源码中使用了装饰器模式,首先,使用WireFormat创建一个Transport
//TcpTransportFactory.class
protected Transport createTransport(URI location, WireFormat wf) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
URI localLocation = null;
String path = location.getPath();
if (path != null && path.length() > 0) {
int localPortIndex = path.indexOf(58);try { Integer.parseInt(path.substring(localPortIndex + 1, path.length())); String localString = location.getScheme() + ":/" + path; localLocation = new URI(localString); } catch (Exception var7) { LOG.warn("path isn't a valid local location for TcpTransport to use", var7.getMessage()); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Failure detail", var7); } } } SocketFactory socketFactory = this.createSocketFactory(); return this.createTcpTransport(wf, socketFactory, location, localLocation); } protected TcpTransport createTcpTransport(WireFormat wf, SocketFactory socketFactory, URI location, URI localLocation) throws UnknownHostException, IOException { return new TcpTransport(wf, socketFactory, location, localLocation); }
最终构建了一个TcpTransport,TcpTransport的构造方法中创建了一个socket(哪里跑),此处传进来的SocketFactory是在TcpTransportFactory中创建的,使用的是DefaultSocketFactory
public TcpTransport(WireFormat wireFormat, SocketFactory socketFactory, URI remoteLocation, URI localLocation) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
this.connectionTimeout = 30000;
this.socketBufferSize = 65536;
this.ioBufferSize = 8192;
this.closeAsync = true;
this.buffOut = null;
this.trafficClass = 0;
this.trafficClassSet = false;
this.diffServChosen = false;
this.typeOfServiceChosen = false;
this.trace = false;
this.logWriterName = TransportLoggerSupport.defaultLogWriterName;
this.dynamicManagement = false;
this.startLogging = true;
this.jmxPort = 1099;
this.useLocalHost = false;
this.stoppedLatch = new AtomicReference();
this.soLinger = -2147483648;
this.wireFormat = wireFormat;
this.socketFactory = socketFactory;try { this.socket = socketFactory.createSocket(); } catch (SocketException var6) { this.socket = null; } this.remoteLocation = remoteLocation; this.localLocation = localLocation; this.initBuffer = null; this.setDaemon(false); }
在DefaultSocketFactory中,创建方法就是单纯实例化一个socket
DefaultSocketFactory() {
}public Socket createSocket() { return new Socket(); }
回到TransportFactory的方法Connect,这时往下
public Transport doConnect(URI location) throws Exception {
try {
Map<String, String> options = new HashMap(URISupport.parseParameters(location));
if (!options.containsKey("wireFormat.host")) {
options.put("wireFormat.host", location.getHost());
}WireFormat wf = this.createWireFormat(options); Transport transport = this.createTransport(location, wf); Transport rc = this.configure(transport, wf, options); IntrospectionSupport.extractProperties(options, "auto."); if (!options.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid connect parameters: " + options); } else { return rc; } } catch (URISyntaxException var6) { throw IOExceptionSupport.create(var6); } }
继续执行this.configure(transport, wf, options);
public Transport configure(Transport transport, WireFormat wf, Map options) throws Exception {
transport = this.compositeConfigure(transport, wf, options);
transport = new MutexTransport(transport);
transport = new ResponseCorrelator(transport);
return transport;
}
发现由对刚刚生成的TcpTransport进行三次包装
第一层包装加入TcpTransport发送数据超时的控制过滤器
public Transport compositeConfigure(Transport transport, WireFormat format, Map options) {
if (options.containsKey("soWriteTimeout")) {
transport = new WriteTimeoutFilter((Transport)transport);
String soWriteTimeout = (String)options.remove("soWriteTimeout");
if (soWriteTimeout != null) {
((WriteTimeoutFilter)transport).setWriteTimeout(Long.parseLong(soWriteTimeout));
}
}IntrospectionSupport.setProperties(transport, options); return (Transport)transport; }
看看WriteTimeoutFilter源码,其存在一个静态成员,完成了加载一个TimeoutThread,并且该类时线程子类,并在构造中完成了对自己的启动
public class WriteTimeoutFilter extends TransportFilter {
protected static ConcurrentLinkedQueue<WriteTimeoutFilter> writers = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
protected static WriteTimeoutFilter.TimeoutThread timeoutThread = new WriteTimeoutFilter.TimeoutThread();
public WriteTimeoutFilter(Transport next) {
super(next);
}
protected static class TimeoutThread extends Thread {
static AtomicInteger instance = new AtomicInteger(0);
boolean run = true;public TimeoutThread() { this.setName("WriteTimeoutFilter-Timeout-" + instance.incrementAndGet()); this.setDaemon(true); this.setPriority(1); this.start(); } public void run() { while(this.run) { boolean error = false; try { if (!interrupted()) { Iterator filters = WriteTimeoutFilter.writers.iterator(); label48: while(true) { WriteTimeoutFilter filter; do { if (!this.run || !filters.hasNext()) { break label48; } filter = (WriteTimeoutFilter)filters.next(); } while(filter.getWriteTimeout() <= 0L); long writeStart = filter.getWriter().getWriteTimestamp(); long delta = filter.getWriter().isWriting() && writeStart > 0L ? System.currentTimeMillis() - writeStart : -1L; if (delta > filter.getWriteTimeout()) { WriteTimeoutFilter.deRegisterWrite(filter, true, (IOException)null); } } } try { Thread.sleep(WriteTimeoutFilter.getSleep()); error = false; } catch (InterruptedException var8) { } } catch (Throwable var9) { if (!error) { WriteTimeoutFilter.LOG.error("WriteTimeout thread unable validate existing sockets.", var9); error = true; } } } } } }
可以看到WriteTimeoutFilter内部维护了一个ConcurrentLinkedQueue保存所有构造的WriteTimeoutFilter对象,在启动的TimeoutThread中,循环迭代检测每个WriteTimeoutFilter对象的输出流是否已经超时,其时通过next.narrow(TimeStampStream.class),也就是TcpTransport中给方法获得一个TimeStampStream对象,从而获得其开始输出的时间
protected TimeStampStream getWriter() {
return (TimeStampStream)this.next.narrow(TimeStampStream.class);
}
//TcpTransport.class
public <T> T narrow(Class<T> target) {
if (target == Socket.class) {
return target.cast(this.socket);
} else {
return target == TimeStampStream.class ? target.cast(this.buffOut) : super.narrow(target);
}
}
如果超时了就会调用deRegisterWrite方法,将WriteTimeoutFilter的socker关闭并从维护的内部集合中删除
protected Socket getSocket() {
return (Socket)this.next.narrow(Socket.class);
}
protected static boolean deRegisterWrite(WriteTimeoutFilter filter, boolean fail, IOException iox) {
boolean result = writers.remove(filter);
if (result && fail) {
String message = "Forced write timeout for:" + filter.getNext().getRemoteAddress();
LOG.warn(message);
Socket sock = filter.getSocket();
if (sock == null) {
LOG.error("Destination socket is null, unable to close socket.(" + message + ")");
} else {
try {
sock.close();
} catch (IOException var7) {
}
}
}return result; }
最终获取到的socket也就是使用TcpTransport中的narrow方法,方法中主要时做一下校验,没问题就返回真实的socket对象(也就是一开始构造时创建的)
public <T> T narrow(Class<T> target) {
if (target == Socket.class) {
return target.cast(this.socket);
} else {
return target == TimeStampStream.class ? target.cast(this.buffOut) : super.narrow(target);
}
}
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public T cast(Object obj) {
if (obj != null && !this.isInstance(obj)) {
throw new ClassCastException(this.cannotCastMsg(obj));
} else {
return obj;
}
}
接下来看到构造函数中调用了super(next),看看其父类TransportFilter的代码
public class TransportFilter implements TransportListener, Transport {
protected final Transport next;
protected TransportListener transportListener;public TransportFilter(Transport next) { this.next = next; } public TransportListener getTransportListener() { return this.transportListener; } public void setTransportListener(TransportListener channelListener) { this.transportListener = channelListener; if (channelListener == null) { this.next.setTransportListener((TransportListener)null); } else { this.next.setTransportListener(this); } } public void start() throws Exception { if (this.next == null) { throw new IOException("The next channel has not been set."); } else if (this.transportListener == null) { throw new IOException("The command listener has not been set."); } else { this.next.start(); } } public void onCommand(Object command) { this.transportListener.onCommand(command); } public void oneway(Object command) throws IOException { this.next.oneway(command); } .....
}
TransportFilter 其实是一个提供模板代码的父类,实现了Transport接口,其中聚合了一个Transport对象作为自己的next(这也符合其Filter的名称,类似过滤器链,带Filter就是带next),TransportFilter 对于接口的实现都是调用next对象的对应方法(因为TransportFilter 聚合的是下一个Transport ),所以真正的实现得看当前具体是TransportFilter的哪个实现,因此我们先记一下Transport 链条的顺序,待会再看是先执行什么方法,毫无疑问的,剩下两个包装类MutexTransport 和ResponseCorrelator 也是TransportFilter的子类(呜呜呜,只有TcpTransport是亲儿子,不用继承TransportFilter,因为传输层是最后的一个呀,不需要next了O(∩_∩)O)
public class MutexTransport extends TransportFilter {
private final ReentrantLock writeLock = new ReentrantLock();
private boolean syncOnCommand;public MutexTransport(Transport next) { super(next); this.syncOnCommand = false; } } public class ResponseCorrelator extends TransportFilter { private final Map<Integer, FutureResponse> requestMap; private IntSequenceGenerator sequenceGenerator; private IOException error; public ResponseCorrelator(Transport next) { this(next, new IntSequenceGenerator()); } }
最终包装下来的Transport就是如下图
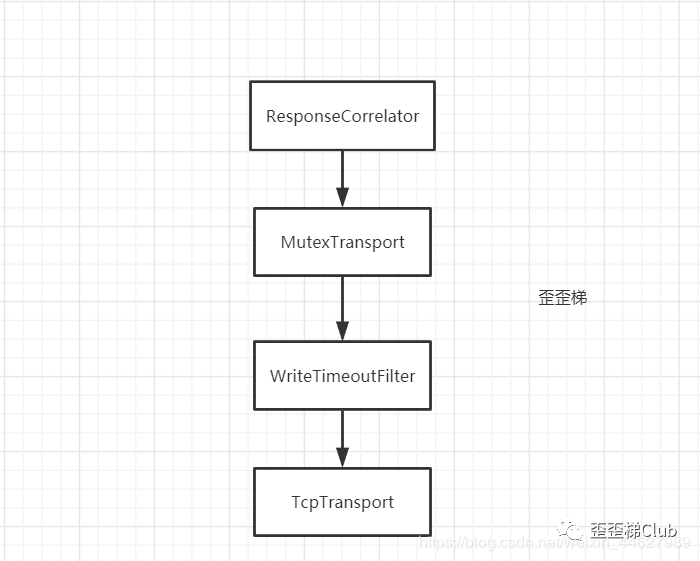
Transport包装顺序
transport.start
回到一开始创建connection那里,发现接下来执行的就是transport的start方法
protected ActiveMQConnection createActiveMQConnection(String userName, String password) throws JMSException {
if (this.brokerURL == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("brokerURL not set.");
} else {
ActiveMQConnection connection = null;
Transport transport = this.createTransport();
connection = this.createActiveMQConnection(transport, this.factoryStats);
connection.setUserName(userName);
connection.setPassword(password);
this.configureConnection(connection);
transport.start();
if (this.clientID != null) {
connection.setDefaultClientID(this.clientID);
}
return connection;
}
这里有个大坑,先是通过createActiveMQConnection创建connecttion,其需要聚合transport,然后我们看connection的实际情况(居然丧心病狂的在构造里将connection的this作为transport的transportListener绑定,这波循环引用,害我找了好久的transportListener),同时TransportFilter的子类对象的setTransportListener方法部署简单的setter,同时会将自己作为next的TransportListener进行绑定(者代码实在难懂)
//ActiveMQConnectionFactory.class
protected ActiveMQConnection createActiveMQConnection(Transport transport, JMSStatsImpl stats) throws Exception {
ActiveMQConnection connection = new ActiveMQConnection(transport, this.getClientIdGenerator(), this.getConnectionIdGenerator(), stats);
return connection;
}
//ActiveMQConnection.class
protected ActiveMQConnection(final Transport transport, IdGenerator clientIdGenerator, IdGenerator connectionIdGenerator, JMSStatsImpl factoryStats) throws Exception {
this.maxThreadPoolSize = DEFAULT_THREAD_POOL_SIZE;
this.rejectedTaskHandler = null;
this.trustedPackages = new ArrayList();
this.trustAllPackages = false;
this.transport = transport;
this.clientIdGenerator = clientIdGenerator;
this.factoryStats = factoryStats;
this.executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 5L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue(), new ThreadFactory() {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, "ActiveMQ Connection Executor: " + transport);
return thread;
}
});
String uniqueId = connectionIdGenerator.generateId();
this.info = new ConnectionInfo(new ConnectionId(uniqueId));
this.info.setManageable(true);
this.info.setFaultTolerant(transport.isFaultTolerant());
this.connectionSessionId = new SessionId(this.info.getConnectionId(), -1L);
this.transport.setTransportListener(this);
this.stats = new JMSConnectionStatsImpl(this.sessions, this instanceof XAConnection);
this.factoryStats.addConnection(this);
this.timeCreated = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.connectionAudit.setCheckForDuplicates(transport.isFaultTolerant());
}
//TransportFilter.class public void setTransportListener(TransportListener channelListener) { this.transportListener = channelListener; if (channelListener == null) { this.next.setTransportListener((TransportListener)null); } else { this.next.setTransportListener(this); }}
所以这时结构如下
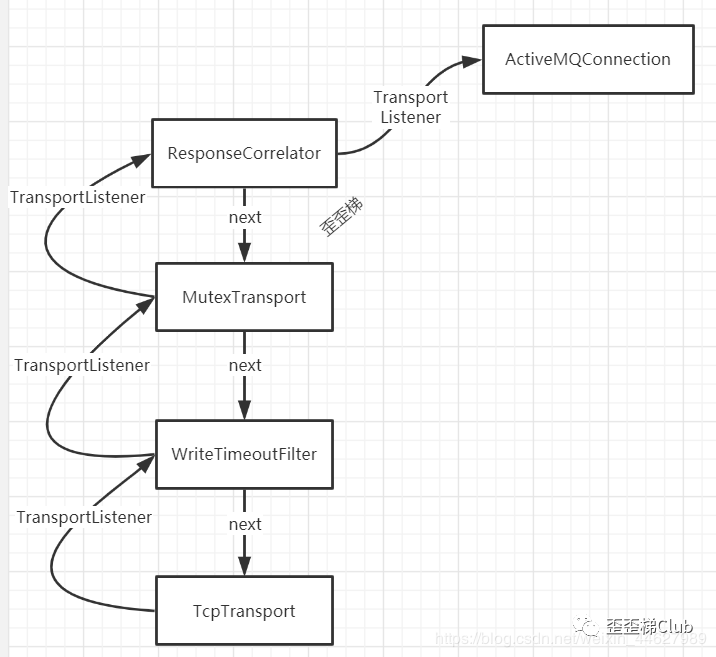
Transport结构 按照包装顺序,此时的transport应该是ResponseCorrelator ,该类中没有该方法,代表这个TransportFilter在start时不需要额外操作,执行父类的start方法,直接调用next的start
//TransportFilter.class
public void start() throws Exception {
if (this.next == null) {
throw new IOException("The next channel has not been set.");
} else if (this.transportListener == null) {
throw new IOException("The command listener has not been set.");
} else {
this.next.start();
}
}
此时就到了MutexTransport,发现里面也没有start,也就是再次走父类TransportFilter的start,继续到next,也就是WriteTimeoutFilter
public void start() throws Exception { super.start(); }public void stop() throws Exception { super.stop(); }
???黑人问号,这里也是没事情做,直接走父类TransportFilter的方法,就是不知道为啥在这里不省略这两个方法,反而是实现,结果还是调用super(秀技?),结果这时就来到TcpTransport了,因为TcpTransport继承了TransportThreadSupport,TransportThreadSupport又继承了TransportSupport,TransportSupport又继承了ServiceTransport,这几个类中唯一实现了start方法的是ServiceTransport,于是进入里面源码
public void start() throws Exception {
if (this.started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
boolean success = false;
this.stopped.set(false);try { this.preStart(); this.doStart(); success = true; } finally { this.started.set(success); } Iterator var2 = this.serviceListeners.iterator(); while(var2.hasNext()) { ServiceListener l = (ServiceListener)var2.next(); l.started(this); } } }
也就是会先调用preStart方法(空实现),然后调用doStart方法,此时执行TcpTransport的doStart方法,完成连接到一开始经过ConnectionFactory传递到TransportFactory再到TcpTransport里的mqtt远程的地址和端口,完成对端口和流的初始化
//TcpTransport.class
protected void doStart() throws Exception {
this.connect();
this.stoppedLatch.set(new CountDownLatch(1));
super.doStart();
}
protected void connect() throws Exception {
if (this.socket == null && this.socketFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot connect if the socket or socketFactory have not been set");
} else {
InetSocketAddress localAddress = null;
InetSocketAddress remoteAddress = null;
if (this.localLocation != null) {
localAddress = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByName(this.localLocation.getHost()), this.localLocation.getPort());
}if (this.remoteLocation != null) { String host = this.resolveHostName(this.remoteLocation.getHost()); remoteAddress = new InetSocketAddress(host, this.remoteLocation.getPort()); } this.trafficClassSet = this.setTrafficClass(this.socket); if (this.socket != null) { if (localAddress != null) { this.socket.bind(localAddress); } if (remoteAddress != null) { if (this.connectionTimeout >= 0) { this.socket.connect(remoteAddress, this.connectionTimeout); } else { this.socket.connect(remoteAddress); } } } else if (localAddress != null) { this.socket = this.socketFactory.createSocket(remoteAddress.getAddress(), remoteAddress.getPort(), localAddress.getAddress(), localAddress.getPort()); } else { this.socket = this.socketFactory.createSocket(remoteAddress.getAddress(), remoteAddress.getPort()); } this.initialiseSocket(this.socket); this.initializeStreams(); } }
接着再调用super.doStart方法也就是TransportThreadSupport中的方法,开启一个线程,将this作为runnable传递并运行
protected void doStart() throws Exception {
this.runner = new Thread((ThreadGroup)null, this, "ActiveMQ Transport: " + this.toString(), this.stackSize);
this.runner.setDaemon(this.daemon);
this.runner.start();
}
因为当前是TcpTransport,所以线程的运行方法是TcpTransport中的run方法,在里面会循环调用doRun方法,根据一开始我们传递进来的协议格式(wireFormat)读取接收到的命令,调用doConsume方法去处理收到的服务端命令消息
public void run() {
LOG.trace("TCP consumer thread for " + this + " starting");
this.runnerThread = Thread.currentThread();try { while(!this.isStopped()) { this.doRun(); } } catch (IOException var7) { ((CountDownLatch)this.stoppedLatch.get()).countDown(); this.onException(var7); } catch (Throwable var8) { ((CountDownLatch)this.stoppedLatch.get()).countDown(); IOException ioe = new IOException("Unexpected error occurred: " + var8); ioe.initCause(var8); this.onException(ioe); } finally { ((CountDownLatch)this.stoppedLatch.get()).countDown(); } } protected void doRun() throws IOException { try { Object command = this.readCommand(); this.doConsume(command); } catch (SocketTimeoutException var2) { } catch (InterruptedIOException var3) { } }
也就是说,此时会开启一个线程,持续读取服务端的命令消息,并处理该消息,因为这时服务端给到客户端的,先了解完客户端发送的逻辑再回来看这个,接下来就到了
//6、使用会话对象创建生产者对象
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(queue);
//7、使用会话对象创建一个消息对象
TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage("hello!test-queue");
//8、发送消息
producer.send(textMessage);
发送消息
前面两个都是创建对象,没啥好说的,主要吧session聚合上了,看看发送消息源码
//ActiveMQMessageProducerSupport.class
private MemoryUsage producerWindow;
public void send(Message message) throws JMSException {
this.send(this.getDestination(), message, this.defaultDeliveryMode, this.defaultPriority, this.defaultTimeToLive);
}
public void send(Destination destination, Message message, int deliveryMode, int priority, long timeToLive, AsyncCallback onComplete) throws JMSException {
this.checkClosed();
if (destination == null) {
if (this.info.getDestination() == null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("A destination must be specified.");
} else {
throw new InvalidDestinationException("Don't understand null destinations");
}
} else {
ActiveMQDestination dest;
if (destination.equals(this.info.getDestination())) {
dest = (ActiveMQDestination)destination;
} else {
if (this.info.getDestination() != null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This producer can only send messages to: " + this.info.getDestination().getPhysicalName());
}dest = ActiveMQDestination.transform(destination); } if (dest == null) { throw new JMSException("No destination specified"); } else { if (this.transformer != null) { Message transformedMessage = this.transformer.producerTransform(this.session, this, message); if (transformedMessage != null) { message = transformedMessage; } } if (this.producerWindow != null) { try { this.producerWindow.waitForSpace(); } catch (InterruptedException var10) { throw new JMSException("Send aborted due to thread interrupt."); } } this.session.send(this, dest, message, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive, this.producerWindow, this.sendTimeout, onComplete); this.stats.onMessage(); } } }
首先调用checkClose检查会话状态,确保不会被关闭了,接着第一步主要是根据你用的Destination是什么?(queue\topic)进行了一下转化为通用的ActiveMQDestination,如果有指定特定的transformer则再进行一下消息的producerTransform,这里没有跳过,接下来核心代码就是
if (this.producerWindow != null) {
try {
this.producerWindow.waitForSpace();
} catch (InterruptedException var10) {
throw new JMSException("Send aborted due to thread interrupt.");
}
}this.session.send(this, dest, message, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive, this.producerWindow, this.sendTimeout, onComplete); this.stats.onMessage();
producerWindow是一个MemoryUsage的对象,主要是记录当前消息堆积了多少内存大小的空间,进行内存的控制,我们看看其部分代码
public class MemoryUsage extends Usage<MemoryUsage> {
private long usage;public void waitForSpace() throws InterruptedException { if (this.parent != null) { ((MemoryUsage)this.parent).waitForSpace(); } this.usageLock.readLock().lock(); try { if (this.percentUsage >= 100 && this.isStarted()) { this.usageLock.readLock().unlock(); this.usageLock.writeLock().lock(); try { while(this.percentUsage >= 100 && this.isStarted()) { this.waitForSpaceCondition.await(); } } finally { this.usageLock.writeLock().unlock(); this.usageLock.readLock().lock(); } } if (this.percentUsage >= 100 && !this.isStarted()) { throw new InterruptedException("waitForSpace stopped during wait."); } } finally { this.usageLock.readLock().unlock(); } }
}
其内部维护一个long类型的成员代表占用内存的字节大小,waitForSpace方法获得字节的读锁进行加锁,判断如果当前使用的内存超过限定内存的100%则改为使用写锁,释放读锁获取写锁,一直等待直到使用的内存小于100%(有空闲可用),此处之所以是>=是因为,没办法刚好处理到100%,可能到了99%,多加一条消息,消息大小超过1%的内存,总而言之,waitForSpace是在等待有空闲的内存,防止消息堆积过多,接下来就进入发送了this.session.send(this, dest, message, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive, this.producerWindow, this.sendTimeout, onComplete);
//ActiveMQSession.class
protected void send(ActiveMQMessageProducer producer, ActiveMQDestination destination, Message message, int deliveryMode, int priority, long timeToLive, MemoryUsage producerWindow, int sendTimeout, AsyncCallback onComplete) throws JMSException {
this.checkClosed();
if (destination.isTemporary() && this.connection.isDeleted(destination)) {
throw new InvalidDestinationException("Cannot publish to a deleted Destination: " + destination);
} else {
synchronized(this.sendMutex) {
this.doStartTransaction();
TransactionId txid = this.transactionContext.getTransactionId();
long sequenceNumber = producer.getMessageSequence();
message.setJMSDeliveryMode(deliveryMode);
long expiration = 0L;
if (!producer.getDisableMessageTimestamp()) {
long timeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
message.setJMSTimestamp(timeStamp);
if (timeToLive > 0L) {
expiration = timeToLive + timeStamp;
}
}message.setJMSExpiration(expiration); message.setJMSPriority(priority); message.setJMSRedelivered(false); ActiveMQMessage msg = ActiveMQMessageTransformation.transformMessage(message, this.connection); msg.setDestination(destination); msg.setMessageId(new MessageId(producer.getProducerInfo().getProducerId(), sequenceNumber)); if (msg != message) { message.setJMSMessageID(msg.getMessageId().toString()); message.setJMSDestination(destination); } msg.setBrokerPath((BrokerId[])null); msg.setTransactionId(txid); if (this.connection.isCopyMessageOnSend()) { msg = (ActiveMQMessage)msg.copy(); } msg.setConnection(this.connection); msg.onSend();//将消息变为只读 msg.setProducerId(msg.getMessageId().getProducerId()); if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) { LOG.trace(this.getSessionId() + " sending message: " + msg); } if (onComplete != null || sendTimeout > 0 || msg.isResponseRequired() || this.connection.isAlwaysSyncSend() || msg.isPersistent() && !this.connection.isUseAsyncSend() && txid == null) { if (sendTimeout > 0 && onComplete == null) { this.connection.syncSendPacket(msg, sendTimeout); } else { this.connection.syncSendPacket(msg, onComplete); } } else { this.connection.asyncSendPacket(msg); if (producerWindow != null) { int size = msg.getSize(); producerWindow.increaseUsage((long)size); } } } } }
可以看到,发送都是会加锁,锁是session里面的sendMutex对象,也就是session是同步处理消息的,然后根据一些配置,选择syncSendPacket(同步发送)或者asyncSendPacket(异步发送),如果使用了异步发送并且有限制堆积的消息大小,此时会维护producerWindow已经使用的内存大小(即堆积的待发送完成消息大小),先看看异步发送吧
//ActiveMQConnection.class
public void asyncSendPacket(Command command) throws JMSException {
if (this.isClosed()) {
throw new ConnectionClosedException();
} else {
this.doAsyncSendPacket(command);
}
}
private void doAsyncSendPacket(Command command) throws JMSException {
try {
this.transport.oneway(command);
} catch (IOException var3) {
throw JMSExceptionSupport.create(var3);
}
}
前面讲过,最外层第一个transport应该是ResponseCorrelator,查看其oneway方法
public void oneway(Object o) throws IOException {
Command command = (Command)o;
command.setCommandId(this.sequenceGenerator.getNextSequenceId());
command.setResponseRequired(false);
this.next.oneway(command);
}
标记了不需要回调,然后进入下一个oneway,也就是MutexTransport,MutexTransport中主要是对其加了一个MutexTransport的写锁,也就是保证了同个connection下消息的同步控制
public void oneway(Object command) throws IOException {
this.writeLock.lock();try { this.next.oneway(command); } finally { this.writeLock.unlock(); } }
接下来到了WriteTimeoutFilter中,前面讲过其维护一个内部集合,并开启一个线程,定期检查该集合中的WriteTimeoutFilter是否超时,此时就是将当前消息加入该集合,再调用下一个oneway(super的实现)
public void oneway(Object command) throws IOException {
try {
registerWrite(this);
super.oneway(command);
} catch (IOException var6) {
throw var6;
} finally {
deRegisterWrite(this, false, (IOException)null);
}}
这时就来的TcpTransport了,进行数据的传输
public void oneway(Object command) throws IOException {
this.checkStarted();
this.wireFormat.marshal(command, this.dataOut);
this.dataOut.flush();
}
因为不需要回调,所以在这里直接就返回了,异步去IO。接下来看看同步发送消息的,可以看到走的是request方法而不是oneway
public Response syncSendPacket(Command command, int timeout) throws JMSException {
if (this.isClosed()) {
throw new ConnectionClosedException();
} else {
try {
Response response = (Response)((Response)(timeout > 0 ? this.transport.request(command, timeout) : this.transport.request(command)));
if (response.isException()) {
ExceptionResponse er = (ExceptionResponse)response;
if (er.getException() instanceof JMSException) {
throw (JMSException)er.getException();
}if (this.isClosed() || this.closing.get()) { LOG.debug("Received an exception but connection is closing"); } JMSException jmsEx = null; try { jmsEx = JMSExceptionSupport.create(er.getException()); } catch (Throwable var8) { LOG.error("Caught an exception trying to create a JMSException for " + er.getException(), var8); } if (er.getException() instanceof SecurityException && command instanceof ConnectionInfo) { try { this.forceCloseOnSecurityException(er.getException()); } catch (Throwable var7) { } } if (jmsEx != null) { throw jmsEx; } } return response; } catch (IOException var9) { throw JMSExceptionSupport.create(var9); } } }
那么进入ResponseCorrelator的request方法,发现实际也是使用asyncRequest异步IO发送,将这个future加入一个内部map,利用Future模型等待结果
public Object request(Object command, int timeout) throws IOException {
FutureResponse response = this.asyncRequest(command, (ResponseCallback)null);
return response.getResult(timeout);
}
public FutureResponse asyncRequest(Object o, ResponseCallback responseCallback) throws IOException {
Command command = (Command)o;
command.setCommandId(this.sequenceGenerator.getNextSequenceId());
command.setResponseRequired(true);
FutureResponse future = new FutureResponse(responseCallback, this);
IOException priorError = null;
synchronized(this.requestMap) {
priorError = this.error;
if (priorError == null) {
this.requestMap.put(new Integer(command.getCommandId()), future);
}
}if (priorError != null) { future.set(new ExceptionResponse(priorError)); throw priorError; } else { this.next.oneway(command); return future; } }
回调处理
Future模型收到回调的逻辑就得回到前面我们讲到的OnCommand方法了,前面讲到,在connection调用start后,外面几个Transport都没干事情,直到TcpTransport的start方法,该start方法会完成连接,并开启一个线程持续调用doRun方法,doRun方法调用readCommand读取收到的服务端发来的命令消息,然后调用doConsume方法,doConsume方法在父类TransportSupport中实现,通过transportListener去处理命令
//TransportSupport.class
public void doConsume(Object command) {
if (command != null) {
if (this.transportListener != null) {
this.transportListener.onCommand(command);
} else {
LOG.error("No transportListener available to process inbound command: " + command);
}
}
}
因为这时TcpTransport的transportListener也就是WriteTimeoutFilter,因为WriteTimeoutFilter没有重写,所以直接走TransportFilter中的实现,继续调用自己的transportListener的onCommand方法
//TransportFilter.class
public void onCommand(Object command) {
this.transportListener.onCommand(command);
}
这时就到了MutexTransport中的onCommand方法
public void onCommand(Object command) {
if (this.syncOnCommand) {
this.writeLock.lock();try { this.transportListener.onCommand(command); } finally { this.writeLock.unlock(); } } else { this.transportListener.onCommand(command); } }
先是判断是否配置了同步的处理回调,如果是就要先拿写锁的锁,最终进入MutexTransport的transportListener的onCommand方法,此时就来到了Transport最外层的ResponseCorrelator的onCommand方法
//ResponseCorrelator.class
//key : commandId
private final Map<Integer, FutureResponse> requestMap;
public void onCommand(Object o) {
Command command = null;
if (o instanceof Command) {
command = (Command)o;
if (command.isResponse()) {
Response response = (Response)command;
FutureResponse future = null;
synchronized(this.requestMap) {
future = (FutureResponse)this.requestMap.remove(response.getCorrelationId());
}if (future != null) { future.set(response); } else if (this.debug) { LOG.debug("Received unexpected response: {" + command + "}for command id: " + response.getCorrelationId()); } } else { this.getTransportListener().onCommand(command); } } else { throw new ClassCastException("Object cannot be converted to a Command, Object: " + o); } }
ResponseCorrelator内部维护了一个存储每个待响应request的集合,再收到服务端消息进入onCommand方法后,根据id获得对应command的future,对该Future进行返回值设置和解锁处理,然后再进入ActiveMQConnection的onCommand方法
public void onCommand(Object o) {
final Command command = (Command)o;
if (!this.closed.get() && command != null) {
try {
command.visit(new CommandVisitorAdapter() {
public Response processMessageDispatch(MessageDispatch md) throws Exception {
ActiveMQConnection.this.waitForTransportInterruptionProcessingToComplete();
ActiveMQDispatcher dispatcher = (ActiveMQDispatcher)ActiveMQConnection.this.dispatchers.get(md.getConsumerId());
if (dispatcher != null) {
Message msg = md.getMessage();
if (msg != null) {
msg = msg.copy();
msg.setReadOnlyBody(true);
msg.setReadOnlyProperties(true);
msg.setRedeliveryCounter(md.getRedeliveryCounter());
msg.setConnection(ActiveMQConnection.this);
msg.setMemoryUsage((MemoryUsage)null);
md.setMessage(msg);
}dispatcher.dispatch(md); } else { ActiveMQConnection.LOG.debug("{} no dispatcher for {} in {}", new Object[]{this, md, ActiveMQConnection.this.dispatchers}); } return null; } public Response processProducerAck(ProducerAck pa) throws Exception { if (pa != null && pa.getProducerId() != null) { ActiveMQMessageProducer producer = (ActiveMQMessageProducer)ActiveMQConnection.this.producers.get(pa.getProducerId()); if (producer != null) { producer.onProducerAck(pa); } } return null; } public Response processBrokerInfo(BrokerInfo info) throws Exception { ActiveMQConnection.this.brokerInfo = info; ActiveMQConnection.this.brokerInfoReceived.countDown(); ActiveMQConnection.this.optimizeAcknowledge = ActiveMQConnection.this.optimizeAcknowledge & !ActiveMQConnection.this.brokerInfo.isFaultTolerantConfiguration(); ActiveMQConnection.this.getBlobTransferPolicy().setBrokerUploadUrl(info.getBrokerUploadUrl()); return null; } public Response processConnectionError(final ConnectionError error) throws Exception { ActiveMQConnection.this.executor.execute(new Runnable() { public void run() { ActiveMQConnection.this.onAsyncException(error.getException()); } }); return null; } public Response processControlCommand(ControlCommand commandx) throws Exception { return null; } public Response processConnectionControl(ConnectionControl control) throws Exception { ActiveMQConnection.this.onConnectionControl((ConnectionControl)command); return null; } public Response processConsumerControl(ConsumerControl control) throws Exception { ActiveMQConnection.this.onConsumerControl((ConsumerControl)command); return null; } public Response processWireFormat(WireFormatInfo info) throws Exception { ActiveMQConnection.this.onWireFormatInfo((WireFormatInfo)command); return null; } }); } catch (Exception var5) { this.onClientInternalException(var5); } } Iterator iter = this.transportListeners.iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()) { TransportListener listener = (TransportListener)iter.next(); listener.onCommand(command); } }
这里使用了适配器模式,传入一个CommandVisitor,visit方法在根据Command是什么具体实现类使用不同实现去决定调用什么方法来处理命令(Command是tcp传输回来消息数据反序列化包装出来的对象,可能是各种类型的消息(包括broker连接,主题删除等,ack处理)),最后的循环主要是如果还设置了一些别的处理TransportListener,则会继续执行对应的onCommand方法(扩展接口)
所以ActiveMQ的完整发送消息的流程如下:
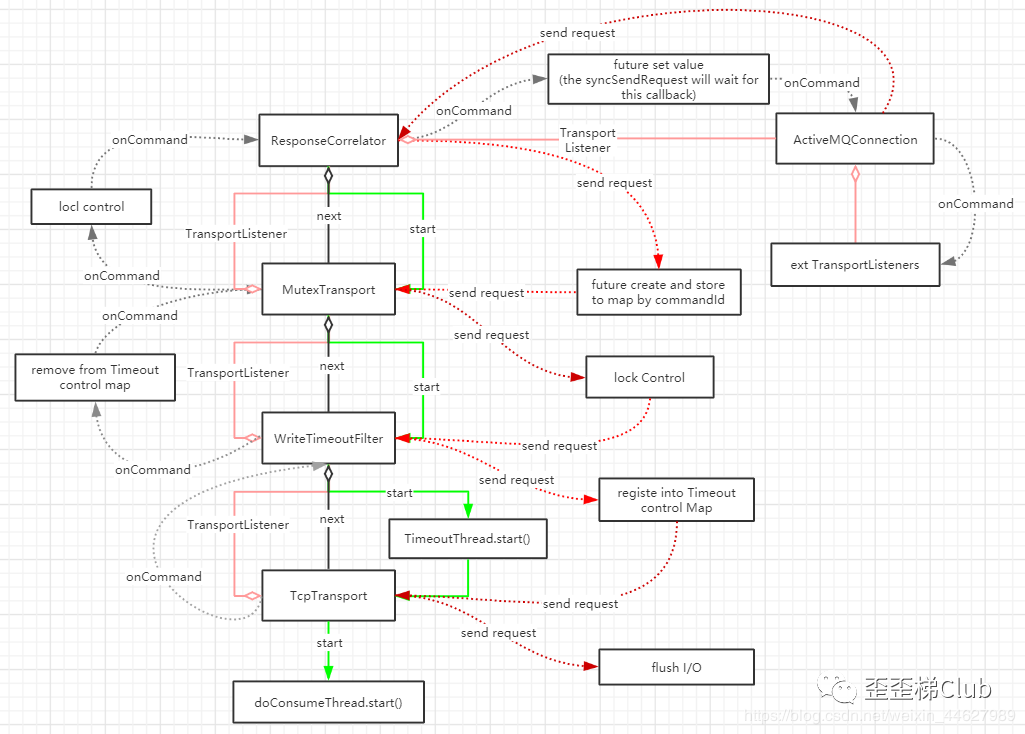
activeMQ流程