来,随我吃透线程池!!!
线程池的作用
线程的创建和销毁的开销是非常大的,线程创建,直接依靠操作系统。大量的线程的创建,会给操作系统和jvm虚拟机带来压力,同时,大量的销毁也会给垃圾回收器带来压力
所以,线程池的目的就是为了解决两个问题
1反复创建线程开销大
2过多的线程太多占用内存
线程池:通过少量线程的复用,成功的解决了这个问题
线程池的好处:
加快响应速度,合理利用cpu与内存,统一管理线程这些线程。
适用线程池的场合
1服务器,服务器要收到大量请求,比如tomcat服务器,也是用线程池实现的
2开发中,5个以上的线程,就可用用线程池了
线程池的创建
- 核心参数配置说明
参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
corePoolSize | 线程池创建的核心线程数,线程池维护线程的最少数量,即使没有任务需要执行,也会一直存活 |
maximumPoolSize | 最大线程池数量,当线程数>=corePoolSize,且任务队列已满时。线程池会创建新线程来处理任务 |
keepAliveTime | 当线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime时,线程会退出,直到线程数量=corePoolSize |
TimeUnit | 时间单位 |
workQueue | 缓存队列(阻塞队列)当核心线程数达到最大时,新任务会放在队列中排队等待执行 |
threadFactory | 线程创建的工厂,一般用默认的 Executors.defaultThreadFactory() |
handler | 当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务 |
这里我们先说一下线程创建的参数,
corePoolsize maxNumPoolSize worekQueue
线程创建,会先创建corePoolsize的线程数量,比如5,当阻塞队列满的时候,比如100,此时线程数量会变大,还处理不过来,就会到maxNumPoolSize最大线程数量,
注意点:弱corePoolSize与maxNumPoolSize保持一致,线程池的大小就是固定的
线程池期望保留线程更少一点,通过corePoolSize在阻塞队列满的时候,才会增加,可以看出来
两个特殊的场景,当阻塞队列大小设置成Integer.MaxValue,那么此时线程数量将不会大于corePoolSize
若maxNumPoolSize设置成Integer.MaxValue,那么此时策略是:允许线程池的容量无限扩大!
keepAliveTime,这里就是多余corePoolSize,大于核心线程数的数量的线程,空闲时间到达这个值 就会被回收

线程工厂,ThreadFactory这个参数直到是创建线程的就可以了,源码这里也无非是new Thread
主要再将一下
工作队列,worKQueue
1)直接交接,SynchronousQueue
2)无界队列:LinkedBlockingQueue
当任务太多,处理不过来,就会导致OOM,内存溢出,而且会让任务丢失
这个队列maxPoolSize是无意义的,因为这个队列满不了
3)有界队列:ArrayBlockingQueue
这个队列是可以满的,maxPoolsize有意义
手动创建or自动创建
有人可能看到过alibaba编码规范

自动创建的话,juc提供了
- JUC包下的Executors工具类提供多种线程池
线程池名称 说明 newFixedThreadPool 一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数 newCachedThreadPool 一个可缓存线程池, newSingleThreadExecutor 一个单线程化的线程池,用唯一的工作线程来执行任务 newScheduledThreadPool 一个定长线程池,支持定时/周期性任务执行
newFixedThreadPool
看名字就能想到,线程池的数量是固定的,那么通过上面的分析,能猜到,核心线程数corePoolSize的数量和maxNumPoolSize最大线程数应该是一致的,
/**
* @Author:Joseph
* @bolg:https://li-huancheng.gitee.io/
* @Package:threadPool
* @Project:bing-fa-demo
* @name:ExecutorDemo
* @Date:2023-07-26 15:03
* @Filename:ExecutorDemo
*/
public class ExecutorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
executorService.execute(new Task());
}
}
}
class Task implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
通过控制台,可以看出,就是编码时候 的4个线程数
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}构造函数中,核心线程数,最大线程数,都是传入的参数nThreads
线程存货时间keepAliveTime是0L,后面的单位就不说了,这个0L,就是,根本没有非核心线程的线程,所以这个参数没什么意义
LinkedBlockQueue,这个工作队列是无限长的,所以当任务量过大的时候,都堆积再linkedBlokQueue阻塞队列中,太多了,内存扛不住,就会出现OOM
package threadPool;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;/**
@Author:Joseph
@Package:threadPool
@Project:bing-fa-demo
@name:FixedThreadPoolExecutorOOM
@Date:2023-07-26 15:34
@Filename:FixedThreadPoolExecutorOOM
*/
public class FixedThreadPoolExecutorOOM {public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
executorService.execute(new SubThread());
}
}
}
class SubThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这是造成OOM的一个小demo,配置下jvm内存小一点就可以看到
newSingleThreadExecutor
这个就不掩饰了,就是暴漏的问题和上面一样,线程存货时间keepAliveLife是没意义的
然后核心线程数和最大线程数是1,阻塞队列采取的是无界队列LinkedBlokingQueue
这两个例子就是阿里巴巴编码规范中说的,大量请求堆积导致的OOM
再看下面两种,
先说下结果
下面两种是创建线程数量太多,大量的线程而导致的OOM
newCachedThreadPool
他的功能是缓存线程池,可回收多余的线程
这个通过上面参数的讲解,可以猜测到,工作队列一定不是无界队列LinkedBlockingQueue,不然线程数量是不会大于corePoolSize核心线程数的
他采用的是SynchronousQueue,直接交换队列,也就是说,这个队列存不了东西,任务直接走到线程去,然后线程不够的话,就直接创建
所以他会导致大量的线程导致oom,线程不用可回收,那么它的keepAliveTime一定配置了个值
现在看一下源码
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}核心线程为0,最大线程无限,keepAliveTime最大存活时间60s,队列采用直接交换队列,队列不缓冲任务
和上面的分析一样
newScheduledThreadPool
支持定时,周期型的执行任务
**
- @Author:Joseph
- @bolg:https://li-huancheng.gitee.io/
- @Package:threadPool
- @Project:bing-fa-demo
- @name:ScheduledThreadPool
- @Date:2023-07-26 15:55
@Filename:ScheduledThreadPool
/
public class ScheduledThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
//4s后再执行
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Task(),4, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//以一定频率重复运行,最开始等1s钟,后面每3s的执行
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Task1(),1,3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
class Task1 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
这里写了下常见 的使用方法
这个既然有线程过多的情况,那么它的maxNumPoolSize最大线程数一定是Integer.MaxValue
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}这里的话,有核心线程数,但是最大线程数是MaxValue,有配置活时间,主要是采用的是延迟工作队列。
这里又多看到一个工作队列
一共有
SynchronousQueue直接交接队列,特点是长度为0
LinkedBlockingQueue无界队列,特点是无界
ArrayBlockingQueue有界队列,特点是有范围
DelayedWorkQueue()延时工作队列,特点是能延迟处理任务
手动创建
看见,jdk提供的,都有bug,都会导致OOM,所以业务使用要自己配置
那么线程池的数量设置成多少何时?
cpu密集型与IO密集型
业务时加密,计算hash等,cpu密集型的话,就可以设置大小为cpu的1~2倍,8核cpu的话,就可以将核心线程数设置为8-16
数据库的读写,文件,网络id这样的,io密集型的话,因为cpu的速度比io快,所以可以将核心线程数设置的多一些,10倍也可以的,
因为80个很多都是在等待io的,所以这样的话才能更好的利用cpu
Brain Goetz大佬就给除了一个公式
线程数= cpu核心数(1+平均等待时间/平均工作时间),当然真实使用的话,还是压测真实环境。估测的话,这个公式就可以的
jdk常见的线程池
通过上面的选择手动创建or自动创建
我们来总结一下jdk提供的线程池
1fixedThreadPool,这种线程池coro和max线程数一致,固定下线程
2cacheThreadPool,这种就是可缓存线程,线程会自动回收
3ScheduleThreadPool.定期执行任务,定时的执行
4singleThreadThreadExcecutor,就是一个线程,
上面我已经讲的很详细了,只需要注意,
1,4会因任务在工作队列的堆积造成OOM
这两个队列的选择就是为了满足需求嘛,线程固定了,那么任务只能通过队列来堆积,所以采用LinedBlocking’queue
2\4会因为线程数量的过大,导致OOM
cachedThreadPool选择SynchronousQueue目的就是全给线程,不需要在队列中转,提高效率
secheduledThread这个的队列就不用说了吧,延时功能
jdk8新的线程池
workStealingPool
特点:子任务 窃取
这里这样理解,三个线程,各个有自己的队列,他们也有公共的队列,
第一个线程自己创建了3个子任务,执行,另外两个线程会帮线程1去执行
这样使用有两个注意,适用不加锁的场景,这样才能让别的线程帮忙执行 ,另外就是执行的顺序不保证,因为会窃取嘛
场景:比较少,
线程池的关闭
线程池的关闭也是有些讲究的!
shutDown
发出线程终止的命令,但是并非是马上的关闭,会等队列中的任务全搞完,就关闭,
同时不会去接受新的任务
isShutDown
判断是否shutDown
isTerminated
这个是判断是否真的关闭了,因为执行shutDown要等待全关掉
awaitTermination
等待一段时间后来判断是否真的关闭
shutDownNow
这个命令会马上关闭,正在执行的线程会中断,在队列中为被消费的,会返回
/**
@Author:Joseph
@bolg:https://li-huancheng.gitee.io/
@Package:threadPool
@Project:bing-fa-demo
@name:ShutDown
@Date:2023-07-28 15:59
@Filename:ShutDown
*/
public class ShutDown {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
executorService.execute(new ShutDownTask());
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
class ShutDownTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}这里就比较简单了,大家自己测试,不是本文的重点
拒接策略
这里回顾一下重要的参数
最大线程数,核心线程数,最大存活时间,工作队列,没错,还有一个就是现在要讲的拒绝策略
拒绝时机
1,当Executior执行shutDown命令,就不会再接受新的任务了
2、工作队列长度,或者最大线程数饱和
四种拒绝策略
AbortPolicy
直接抛出异常
DiscardPolicy
丢弃新的任务,我们是不知道的!
DiscardPolicyOldestPolicy
这个是丢掉最老的任务。
CallerRunsPolicy
让提交任务的线程去执行,比如异步功能,想要让线程池去做,但是线程池饱和了,线程池说,我不做,你自己做,这个就是CallerRunsPolicy,这个就是不像被压榨的员工哈哈
钩子函数
我们想在每个任务执行前后做一些日志统计,等任务,比如暂停,实现一个暂停的线程池
package threadPool;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
-
延时每个任务执行的前后都可以放钩子函数
-
@Author:Joseph
-
@Package:threadPool
-
@Project:bing-fa-demo
-
@name:PauseableThreadPool
-
@Date:2023-07-28 16:31
@Filename:PauseableThreadPool
*/
public class PauseableThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor {private final ReentrantLock lock= new ReentrantLock();
private Condition unpaused = lock.newCondition();
private boolean isPaused;
public PauseableThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}public PauseableThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory);
}public PauseableThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler);
}public PauseableThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
}@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
lock.lock();
try{
while(isPaused){
unpaused.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}private void pause(){
lock.lock();
try{
isPaused = true;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}public void resume(){
lock.lock();
try{
isPaused=false;
unpaused.signalAll();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
PauseableThreadPool pauseableThreadPool = new PauseableThreadPool(10, 20, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我被执行");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pauseableThreadPool.execute(runnable);} Thread.sleep(1500); pauseableThreadPool.pause(); System.out.println("线程池被暂停了"); Thread.sleep(1500); pauseableThreadPool.resume(); System.out.println("线程池恢复了");}
}
线程池实现源码
上面了解了下线程池的使用注意点,现在看下线程池怎么实现的
线程池的组成部分
线程池管理器:创建、管理线程池
工作线程:就是线程池中存在的线程
任务队列:这个就是参数里重要之一的工作队列,因为并发嘛,多个线程去取线程,所以采用的阻塞队列blokingQueue
任务接口(Task):这个就是线程池要执行的一个一个的任务
Executor家族的区分
ThreadPoolExecutor、ExecutorService、Executor、Executors

这是他们的继承实现关系
Executor
public interface Executor {
/**
- Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
- may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
- thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation.
- @param command the runnable task
- @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
- accepted for execution
@throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
void execute(Runnable command);
}
Executor是一个顶级的接口,只有这一个execute的方法
ExecutorService
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
void shutdown();
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
boolean isShutdown();
boolean isTerminated();
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
ExecutorService继承了Executor,并新增了一些管理线程池的方法
Executors
一个工具类这里就不多说了,上面讲解的很透彻,只是调用创建线程池的构造函数,指定一些规则而已
ThreadPoolExecutor
这里就要着重讲一下了,这里他是ExecutorService的实现,返回值是ExecutorService
也是我们开发人员调用这个构造函数自定义线程池使用的,文章末尾会带大家实操一下
public class ThreadPoolTaskExecutor extends ExecutorConfigurationSupport implements AsyncListenableTaskExecutor, SchedulingTaskExecutor {
private final Object poolSizeMonitor = new Object();
private int corePoolSize = 1;
private int maxPoolSize = 2147483647;
private int keepAliveSeconds = 60;
private int queueCapacity = 2147483647;
private boolean allowCoreThreadTimeOut = false;线程池如何实现线程的复用
这是ThreadPoolExecutor中额execute方法
org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();int c = ctl.get(); //线程不够,增加线程 if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) { //我们要看的就是wordker方法 if (addWorker(command, true)) return; c = ctl.get(); } if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) { int recheck = ctl.get(); if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command)) reject(command); else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0) addWorker(null, false); } else if (!addWorker(command, false)) reject(command); }</code></pre></div></div><p>好,看一下work中的runWorker方法</p><p>java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor#runWorker</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">final void runWorker(Worker w) { Thread wt = Thread.currentThread(); //注意这里的task,Runnable的run方法就是一个一个的类 Runnable task = w.firstTask; w.firstTask = null; w.unlock(); // allow interrupts boolean completedAbruptly = true; try { //主要看这里,如果task不为null,就去执行这里的逻辑,getTask就是从阻塞队列中拿出任务 //while循环代表,这个work不会停止,执行完任务就会继续拿下一个任务去执行,这就实现了线程的复用 while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) { w.lock(); // If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted; // if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This // requires a recheck in second case to deal with // shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) || (Thread.interrupted() && runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) && !wt.isInterrupted()) wt.interrupt(); try { beforeExecute(wt, task); try { //这里就是调用runnable的run方法, task.run(); afterExecute(task, null); } catch (Throwable ex) { afterExecute(task, ex); throw ex; } } finally { task = null; w.completedTasks++; w.unlock(); } } completedAbruptly = false; } finally { processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly); } }</code></pre></div></div><h3 id="fchf8" name="%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B%E6%B1%A0%E7%9A%84%E7%8A%B6%E6%80%81">线程池的状态</h3><div class="table-wrapper"><table><thead><tr><th style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-header"><p>状态</p></div></div></th><th style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-header"><p>说明</p></div></div></th></tr></thead><tbody><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>RUNNING</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>运行状态,能接受新提交的任务,并且也能处理阻塞队列中的任务</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>SHUTDOWN</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>关闭状态,不再接受新提交的任务,可以继续处理阻塞队列中已保存的任务。</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>STOP</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>不能接受新任务,也不处理队列中的任务,会中断正在处理任务的线程</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>TIDYING</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>所有的任务都已终止了,workerCount (有效线程数)为0</p></div></div></td></tr><tr><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>TERMINATED</p></div></div></td><td style="text-align:left"><div><div class="table-cell"><p>terminated() 方法执行完后进入该状态</p></div></div></td></tr></tbody></table></div><p>通过上面线程关闭的学习,再结合这里看一下</p><p>shutDown会使Running状态到SHUTDOWN状态,线程池会拒绝新任务,但是还是会执行新的任务</p><p>shutDOwnNow让线程池从Running状态到STOP状态,此时拒绝新任务,同时也会中断正在执行的任务,同时会返回队列中的任务</p><p>当上面两种方法执行完,队列和工作线程都空时,会进入tidying状态,执行termined会进入TERMINATED关闭状态。</p><p>在这里站在上帝视角看下源码</p><p>无非就是</p><p>execute、addworker 、runworker、getTask方法</p><p>这里要先将一下,ctl这个</p><p>变量 <code>ctl</code>这个AtomicInteger包含两部分的信息,使用的是位运算的方式,相比于基本运算,速度快很多</p><ul class="ul-level-0"><li>运行状态 (runState) 高3位保存</li><li>线程池内有效线程的数量 (workerCount),低29位保存</li></ul><p>下面是变量和比较重要的方法</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService { /** * workerCount, indicating the effective number of threads * runState, indicating whether running, shutting down etc * RUNNING -> SHUTDOWN * On invocation of shutdown() * (RUNNING or SHUTDOWN) -> STOP * On invocation of shutdownNow() * SHUTDOWN -> TIDYING * When both queue and pool are empty * STOP -> TIDYING * When pool is empty * TIDYING -> TERMINATED * When the terminated() hook method has completed * */ //int类型的数字,高3位表示线程池状态,低29位表示worker数量 private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0)); //Integer.SIZE`为32,所以`COUNT_BITS`为29 private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3; //线程池允许的最大线程数, 1左移29位,然后减1,即为 2^29 - 1 private static final int COUNT_MASK = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1; // runState is stored in the high-order bits private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS; private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS; private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS; private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS; private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS; //获取线程池状态 private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~COUNT_MASK; } //获取线程池worker数量 private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & COUNT_MASK; } //根据线程池状态和线程池worker数量,生成ctl值 private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }</code></pre></div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">//任务执行public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 32位,高3位存储线程池状态,低29位存储活跃线程数
int c = ctl.get();
//判断工作线程小于核心线程,则创建新线程,true表示是核心线程数
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
//判断线程池是否运行,把任务放到队列里面去,返回boolean状态
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
//再次获取值
int recheck = ctl.get();
//如果线程池已经终止,则移除任务,不在响应
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
//如果没有线程,则创建一个空的worker,会从队列获取任务执行
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
//队列满后,调用addWorker,创建非核心线程,参数是false,
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
//队列已满,创建非核心线程,失败则执行拒绝策略
reject(command);
}//用于向线程池中添加一个新的工作线程。如果线程池中的线程数量已经达到maximumPoolSize,则返回false;
//如果线程池已经关闭,则返回false;否则,创建一个新的工作线程,并将其加入工作线程集合中
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (int c = ctl.get();;) {
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (runStateAtLeast(c, SHUTDOWN)
&& (runStateAtLeast(c, STOP)
|| firstTask != null
|| workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;for (;;) { //判断线程数,根据传进来参数判断是创建线程数最大值 if (workerCountOf(c) >= ((core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize) & COUNT_MASK)) return false; //增加worker数量成功,返回到上面的retry if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c)) break retry; c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl if (runStateAtLeast(c, SHUTDOWN)) continue retry; // else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop } } boolean workerStarted = false; boolean workerAdded = false; Worker w = null; try { w = new Worker(firstTask); final Thread t = w.thread; if (t != null) { final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock; mainLock.lock(); try { // Recheck while holding lock. // Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if // shut down before lock acquired. int c = ctl.get(); if (isRunning(c) || (runStateLessThan(c, STOP) && firstTask == null)) { if (t.getState() != Thread.State.NEW) throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); workers.add(w); workerAdded = true; int s = workers.size(); if (s > largestPoolSize) largestPoolSize = s; } } finally { mainLock.unlock(); } //新创建的worker,然后立刻启动,立刻执行任务(不是从队列中获取) if (workerAdded) { t.start(); workerStarted = true; } } } finally { if (! workerStarted) addWorkerFailed(w); } return workerStarted; }//用于执行指定的工作线程,首先获取当前线程,然后不断从阻塞队列中取出任务并执行,直到从阻塞队列中取出null为止。
//在每次执行任务之前,会调用beforeExecute()方法和afterExecute()方法,这两个方法可以由子类进行重写,以实现一些特定的功能。final void runWorker(Worker w) { Thread wt = Thread.currentThread(); Runnable task = w.firstTask; w.firstTask = null; w.unlock(); // allow interrupts boolean completedAbruptly = true; try { //一直循环判断,当前任务是否有,没的话getTask()从队列中获取任务执行 while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) { w.lock(); // If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted; // if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This // requires a recheck in second case to deal with // shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) || (Thread.interrupted() && runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) && !wt.isInterrupted()) wt.interrupt(); try { beforeExecute(wt, task); try { task.run(); afterExecute(task, null); } catch (Throwable ex) { afterExecute(task, ex); throw ex; } } finally { task = null; w.completedTasks++; w.unlock(); } } completedAbruptly = false; } finally { processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly); } }//用于从阻塞队列中获取一个任务,如果当前线程数小于corePoolSize,则会调用workQueue的take方法阻塞在当前
private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false; // Did the last poll() time out?for (;;) { int c = ctl.get(); // Check if queue empty only if necessary. if (runStateAtLeast(c, SHUTDOWN) && (runStateAtLeast(c, STOP) || workQueue.isEmpty())) { decrementWorkerCount(); return null; } int wc = workerCountOf(c); // timed用于超时控制,当allowCoreThreadTimeOut是true或者活跃线程数大于核心线程数,则需要进行超时控制 boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize; if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut)) && (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) { if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c)) return null; continue; } //take和poll都是从队列头部【拿出】一个元素,从头部得到并移除该元素 //poll空队列的头部元素时返回null,不抛异常;而take方法对应获得空队列的头部元素时,会阻塞在获取的位置 try { Runnable r = timed ? workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) : workQueue.take(); if (r != null) return r; timedOut = true; } catch (InterruptedException retry) { timedOut = false; } } }</code></pre></div></div><p>关于源码的解读,大家看注释就可以</p><p>我想着重点一下,这个阻塞队列,take方法,这里就体现阻塞队列的特性了,take方法,不会返回元素,而是阻塞,</p><p>还有就是work类中的works,本质是一个HashSet集合</p><figure class=""><div class="rno-markdown-img-url" style="text-align:center"><div class="rno-markdown-img-url-inner" style="width:83.93%"><div style="width:100%"><img src="https://cdn.static.attains.cn/app/developer-bbs/upload/1722963925354679855.png" /></div><div class="figure-desc">image-20230728203619289</div></div></div></figure><p>再者需要注意runworker中执行前后的两个钩子</p><figure class=""><div class="rno-markdown-img-url" style="text-align:center"><div class="rno-markdown-img-url-inner" style="width:83.93%"><div style="width:100%"><img src="https://cdn.static.attains.cn/app/developer-bbs/upload/1722963925756821685.png" /></div><div class="figure-desc">image-20230728203836873</div></div></div></figure><p>前面提到,核心线程数是不会消失的,但是,这里指的是永远是数量,HashSet这里并没有区分线程是先创建的还是后创建的,</p><p>所以core核心线程数为3,假设有6个,剩下来的3个不一定是最初创建的线程!</p><h2 id="bl749" name="%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E4%B8%BA%E7%8E%8B">实战为王</h2><p>这里讲一下工作中,如何创建线程池</p><p>先看一下,使用线程池的注意点</p><p>避免任务堆积</p><p>避免线程数过度增加</p><p>排查线程泄漏(线程回收不了的情况):一般是任务逻辑问题,导致任务结束不了,导致任务回收不了</p><p>如果有人问:工作中线程池是怎样做的?我认为可以这样回答</p><p>线程数的配置,要考虑io密集型和cpu密集型,io密集型可以设置2倍的核数,cpu密集型最好是和核数相等</p><p>阻塞队列的长度可以区分面向C端的快速响应还是面向B端的允许慢速处理的场景</p><p>C端的阻塞队列长度不能太长,另外C端,可以通过多节点,来增快消费速度,避免堆积,B端可以长一些</p><p>当然要结合业务,进行多接口压测,才能得到合理的数据。</p><p>这里列举两个场景。(以32核,64g为例)</p><p>C端:</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 32, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(100000), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());</code></pre></div></div><p>这个C端的场景,就没有考虑上面说的,阻塞队列太长了,而核心线程数有过短,所以这里,就会出现问题,任务堆积而得不到消费</p><p>C端的场景不应该设置过长的策略,且要注意消费的速度要大一些</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(32,128, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1000), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());</code></pre></div></div><p>一台机器不够,那就多一些</p><p>B端</p><p>商家管理后台统计报表</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(8,1024, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1000), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());</code></pre></div></div><p>这里没有考虑B端场景,队列可以长一些,因为不要求实时性,这样配置,1024线程,导致OOM,服务器崩溃</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(32,124, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(100000), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());</code></pre></div></div><p>这样配置,让任务能过慢慢处理,同时队列又不是长的很过分,100万,并不会出现OOM的问题</p><p>另外</p><p>生产配置的时候,要线程池的隔离,不能让多个不同任务公用线程池,</p><h2 id="advmj" name="%E5%BC%82%E6%AD%A5%E6%8F%90%E9%AB%98qps">异步提高qps</h2><p>到这里,线程池基本就完结了</p><p>这里提供之前做项目的一个场景,这里用到了http连接池,和线程池,通过这个例子,我们看一下,工作中,如何用线程池,以及考虑引发的一些问题,</p><h3 id="a8hke" name="%E5%BC%82%E6%AD%A5%E7%9A%84%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%BB%A5%E5%8F%8A%E4%B8%80%E4%BA%9B%E6%B3%A8%E6%84%8F%E4%BA%8B%E9%A1%B9">异步的使用场景以及一些注意事项</h3><p>涉及网络通信,且有需要提高响应速度,就可以用异步,</p><p>MQ也属于一种异步,</p><p>适用于处理log,发送邮件,短信–等场景,涉及网络io调用,并不影响业务,因为异步是直接返回正常的,不知道后面是否成功</p><p>使用方式:启动类,开启异步@EnableAsync </p><p>异步失效场景:</p><p>异步采用动态代理,不能调用类本身的方法,加@Async,</p><ul class="ul-level-0"><li>注解@Async的方法不是public方法</li><li>注解@Async的返回值只能为void或者Future</li><li>注解@Async方法使用static修饰也会失效</li></ul><p>还要注意事物,@Tranctional与@Async会失效,但是,在调用异步的上游,就没事</p><h3 id="fkaen" name="%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B%E6%B1%A0">线程池</h3><p>当我们使用@Async的时候,没有自定义线程池,他会使用默认的线程池</p><p>默认8个核心线程数,核心线程处理不了,就会进入阻塞队列,阻塞队列是默认的Integer.MAX_VALUE,21亿!采用的是LinkedBlokingQueue,最大线程数也是21亿,但是根本不会大于8,因为阻塞队列满了才会到达,但是不可能满的</p><p>所以就要自定义线程池,</p><p>但是!</p><p>在spring中,自定义线程池要用ThreadPoolTaskExecutor,其实是一样的,只是框架多了层包装而已</p><p>我们只需要自定义线程池,覆盖spring默认的线程池,就能避免OOM的问题了</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">Configuration@EnableAsync
public class ThreadPoolTaskConfig {@Bean("threadPoolTaskExecutor") public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor(){ ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); //线程池创建的核心线程数,线程池维护线程的最少数量,即使没有任务需要执行,也会一直存活 //如果设置allowCoreThreadTimeout=true(默认false)时,核心线程会超时关闭 executor.setCorePoolSize(16);// executor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
//缓存队列(阻塞队列)当核心线程数达到最大时,新任务会放在队列中排队等待执行 executor.setQueueCapacity(1024); //最大线程池数量,当线程数>=corePoolSize,且任务队列已满时。线程池会创建新线程来处理任务 //当线程数=maxPoolSize,且任务队列已满时,线程池会拒绝处理任务而抛出异常 executor.setMaxPoolSize(64); //当线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime时,线程会退出,直到线程数量=corePoolSize //允许线程空闲时间60秒,当maxPoolSize的线程在空闲时间到达的时候销毁 //如果allowCoreThreadTimeout=true,则会直到线程数量=0 executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(30); executor.setThreadNamePrefix("joseph的自定义线程池"); //拒绝策略 // rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务 // CallerRunsPolicy():交由调用方线程运行,比如 main 线程;如果添加到线程池失败,那么主线程会自己去执行该任务,不会等待线程池中的线程去执行 //AbortPolicy():该策略是线程池的默认策略,如果线程池队列满了丢掉这个任务并且抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。 //DiscardPolicy():如果线程池队列满了,会直接丢掉这个任务并且不会有任何异常 //DiscardOldestPolicy():丢弃队列中最老的任务,队列满了,会将最早进入队列的任务删掉腾出空间,再尝试加入队列 executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); executor.initialize(); return executor; }
}
好,我们异步的时候
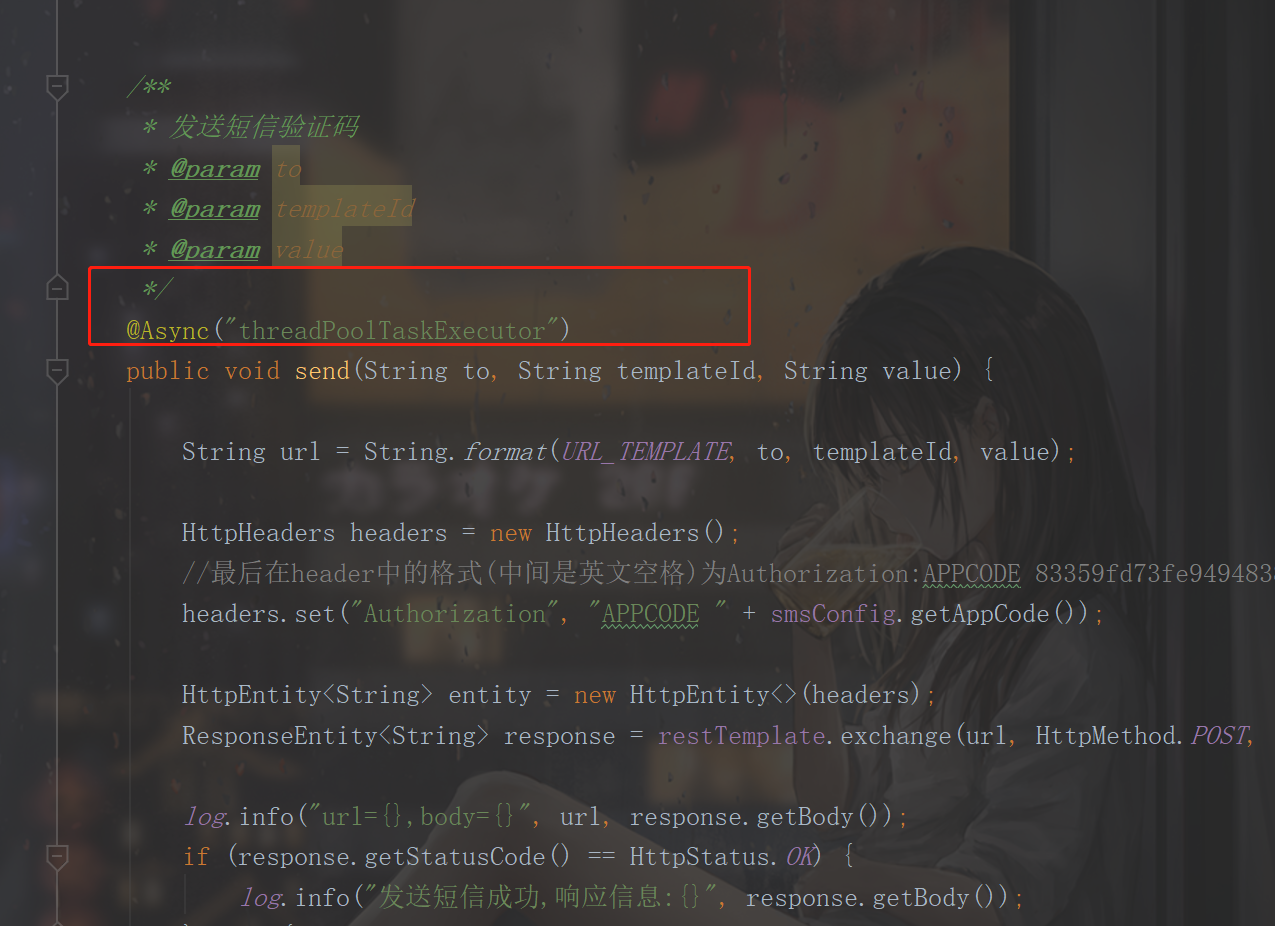
直接指定线程池
@Async(“threadPoolTaskExecutor”)就可以了
好,那么当请求量很多的时候,就会引发问题
导致OOM,服务器重启,是会丢失的!,或者说,阻塞队列你设置的短一些的话,任务也是会丢失的(拒绝策略的话)
意思就是,我们不能单单的把任务堆到队列就好了,是会有消息丢失的风险的!
对的,就是提高线程处理任务的速度!
消费方角度提高
当涉及网络请求时,spring中使用的是restTempate
这是spring基于httpClient提供的一个http请求工具,我们异步发短信调用第三方服务,用到restTemplate,但是restTemplate在spring中有个坑,
- 底层通过使用java.net包下的实现创建HTTP 请求
- 通过使用ClientHttpRequestFactory指定不同的HTTP请求方式,主要提供了两种实现方式
- SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory(默认)
- 底层使用J2SE提供的方式,既java.net包提供的方式,创建底层的Http请求连接
- 主要createRequest 方法( 断点调试),每次都会创建一个新的连接,每次都创建连接会造成极大的资源浪费,而且若连接不能及时释放,会因为无法建立新的连接导致后面的请求阻塞
- HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory
- 底层使用HttpClient访问远程的Http服务
- SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory(默认)
这就导致,每次请求都会三次握手,非常的耗时,
当请求处理不过来,客户端等待过长,主动断掉连接,就会报错
错误Caused by: java.io.IOException: Broken pipe
- 服务端向前端socket连接管道写返回数据时 链接(pipe)却断开了
我们可以通过http连接池的方式,来服用建立 的连接,来加快线程处理的速度
进而加快阻塞队列的消费
对httpclient进行封装的有:Apache的Fluent、es的restHighLevelClient、spring的restTemplate等
这几个都可以进行http连接池的封装!
下面来看一下,如何封装
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {@Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate(ClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory){ return new RestTemplate(requestFactory); } @Bean public ClientHttpRequestFactory httpRequestFactory(){ return new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpClient()); } @Bean public HttpClient httpClient(){ Registry<ConnectionSocketFactory> registry = RegistryBuilder.<ConnectionSocketFactory>create() .register("http", PlainConnectionSocketFactory.getSocketFactory()) .register("https", SSLConnectionSocketFactory.getSocketFactory()) .build(); PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager connectManager = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager(registry); //设置连接池最大是500个链接 connectManager.setMaxTotal(500); //maxPerToute对maxTotal细分 每个主机最大并发是300 route是指域名 connectManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(300); RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom() //返回数据超时时间 .setSocketTimeout(20000) //连胜服务器超时时间 .setConnectTimeout(10000) //从连接池中获取连接的超时时间 .setConnectionRequestTimeout(1000) .build(); CloseableHttpClient closeableHttpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig) .setConnectionManager(connectManager) .build(); return closeableHttpClient; } //优化前
// @Bean
// public ClientHttpRequestFactory simpleClientHttpRequestFactory(){
// SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory();
// factory.setReadTimeout(10000);
// factory.setConnectTimeout(10000);
// return factory;
// }
}
现在,要涉及网络调用,异步提高性能的话
就没有任何问题了!
总结就是,先发现异步请求在压测的时候,会导致OOM,然后再自定义线程池,但是处理太慢,有超时报错和http管道报错,我们又更换httpClient,自定义http连接池,最终完成了qps的提高