❝写到前面:故虽然我事前也查阅了许许多多的博客专栏书籍,但是由于很多教程都是几年以前的,其不少插件或loader均进行了升级迭代不再是以前的用法,其新的使用方法均需一个一个手动查询。如有误,望指教。感恩! ❞
写在开头 我想这些你应该事先知道

1. webpack是干什么的,它如今在前端是一个什么样的地位
这个其实不用多说了,如今的前端项目哪里还有用不到打包工具的呢,而webpack又作为打包工具中的王者我们又有什么理由不去搞明白它呢。
2. commonjs与ES6 Module不应该了解吗
先简单说一下吧
通常node中便是使用commonjs,其导入使用require,导出使用module.exports
ES6 Module中即导入使用import,导出则有两种
- 命名导出export
- 默认导出export default,对外输出了一个名为default的变量,因此不需要像命名导出一样进行变量声明,直接导出值即可。一个文件只能有一个
注意注意的是:在导入一个模块时,对于CommonJS来说获取的是一份导出值的拷贝;而在ES6 Module中则是值的动态映射,并且这个映射是只读的。
还有一些AMD和UMD,模块的东西先了解到这里吧。毕竟这里是为webpack做铺垫的
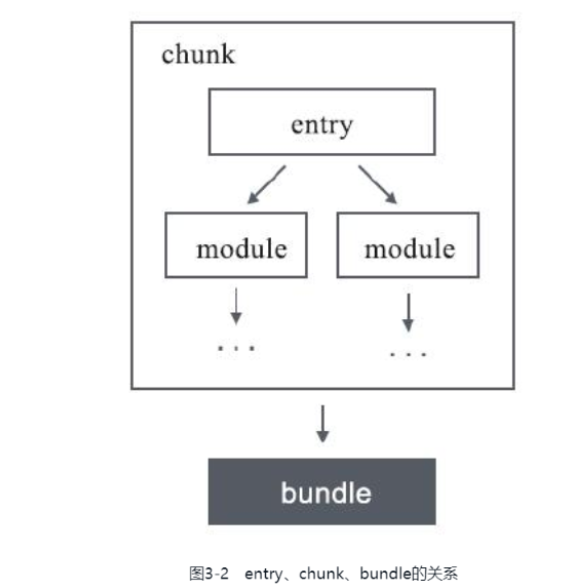
3. entry&chunk&bundle之间的关系
这张图已经很明确了吧
4 webpack中的核心概念
entry
用于指定本次webpack打包的地址(相对地址即可)如:
单入口 entry:'./src/index.js' 或: entry:{ main:'./src/index.js' }
多入口
entry:{
main:'./src/index.js',
other:'./src/other.js'
}
output
用于指定打包完成之后的输出文件地址及文件名,文件地址使用绝对地址
单文件
output:{
filename:'bundle.js',
path:path.join(__dirname,'dist')
}
多文件
output:{
filename:'[name].js',
path:path.join(__dirname,'dist')
}
mode
用于指定当前构建环境
主要有以下三种选择
- production
- development
- none
设置mode会自动触发webpack的一些内置函数,不写默认为none
loaders
webpack默认是能识别.json、.js、模块,其他模块我们需要借助loaders帮助我们将它们放进依赖图里面
它本质就是一个函数,接收源文件为参数,返回转换后的结果
plugins
plugin可以在webpack运行到某个阶段的时候(webpack利用tapable搞了许多生命周期的构造,方便我们在合适的时间利用插件帮我们做些合适的事情),做一些我们需要的事情。如clean-webpack-plugin会在我们进打包的时候先删除dist下的原输出文件。

一:基础使用
1.1 处理html、css、js
使用webpack-dev-server
我们也是希望自己打包后文件可以在一个本地服务器上启动,webpack-dev-server就是一个这种东西。
安装:npm i webpack-dev-server -D
「新配置webpack.config.js一个devServer属性」
如下:
devServer: {
port: 3000,
contentBase: './dist' // 起服务的地址(即定位到我们的输出文件地址)
open: true // 自动打开浏览器
compress:true // gzip压缩
}「为简化命令在package.json中添加一个dev命令」
同时也可以在配一个打包命令,不过我一般喜欢用npx
{
"name": "webpack-test02",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"build":"webpack",
"dev": "webpack-dev-server",
},
}使用html-webpack-plugin
可能上面你发现了,没有一个html文件。即使服务器启动也没有什么卵用,接下来我们可以在文件中写一个html模板(只生成骨架即可)然后利用html-webpack-plugin将这个模板同时打包到dist目录下,并引入输出的bundl.js
安装:npm i html-webpack-plugin -D
使用:
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',//模板文件地址
filename: 'index.html',//指定打包后的文件名字
hash: true,//也可给其生成一个hash值}), ], 还有以下选项
minify: { // 压缩打包后的html文件
removeAttributeQuotes: true, // 删除属性双引号
collapseWhitespace: true // 折叠空行变成一行
}
处理css
基本处理
这里需要安装两个loader,即css-loader(用于处理css中的@import这种语法)、style-loader用于将css插入head标签
安装:npm i css-loader style-loader -D
使用:
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.css$/,
use: ['style-loader','css-loader']
},] }或指定参数,下面是每次将css插入到head标签的前面。以保证我们后面自己在模板中的设置可覆盖
module: {
rules: [{
test: /.css$/,
use: [{
loader: 'style-loader',
options: {
insert: function insertAtTop(element) {
var parent = document.querySelector('head');
// eslint-disable-next-line no-underscore-dangle
var lastInsertedElement =
window._lastElementInsertedByStyleLoader;if (!lastInsertedElement) { parent.insertBefore(element, parent.firstChild); } else if (lastInsertedElement.nextSibling) { parent.insertBefore(element, lastInsertedElement.nextSibling); } else { parent.appendChild(element); } // eslint-disable-next-line no-underscore-dangle window._lastElementInsertedByStyleLoader = element; }, } }, 'css-loader' ] }, ]}</code></pre></div></div><h6 id="1dlqv" name="%E6%8A%BD%E7%A6%BBcss"><strong>抽离css</strong></h6><p>使用插件 <code>mini-css-extract-plugin</code></p><p>安装:<code>npm i mini-css-extract-plugin -D</code></p><p>抽离成了单文件即不需要在用<code>style-loader</code>了</p><p>使用:</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">const MinniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin') plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ // 指定模板文件 template: './src/index.html', // 指定输出的文件名 filename: 'index.html', // 添加hash解决缓存 }), new MinniCssExtractPlugin({ //指定输出的文件名 filename: 'main.css' }) ], module: { rules: [{ test: /\.css$/, use: [ MinniCssExtractPlugin.loader,//本质就是创建一个style标签再将输出的css地址引入 'css-loader', ] }, ] }</code></pre></div></div><h6 id="59m74" name="%E5%8E%8B%E7%BC%A9css%E3%80%81js"><strong>压缩css、js</strong></h6><p>将上面输出的css文件做压缩处理</p><p>使用插件<code>optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin</code>但是使用了此插件压缩css之后,js需要使用<code>uglifyjs-webpack-plugin</code>继续压缩</p><p>安装:<code>npm i optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin uglifyjs-webpack-plugin -D</code></p><p>使用:(注意此插件不再在plugin中使用了,使用位置为优化<code>optimization</code>属性里面)</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">const OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new UglifyJsPlugin({
cache: true,
parallel: true,
sourceMap: true
}),
new OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin({})
]
},
添加厂商前缀
需要一个loader和一个样式工具:postcss-loader autoprefixer
「先来说一下什么是postCss」
它是一个编译插件的容器,它的工作模式为接收源代码交由编译插件处理,最后输出css。
postcss-loader就是postCss和webpack的连接器。postcss-loader可以和css-loader一起使用也可以单独使用。注意单独使用postcss-loader的使用css中不建议使用@import语法,否则会产生冗余代码。
postCss还还需要一个单独的配置文件postcss.config.js
下面还看用post-loader和autoprefixer 来生成厂商前缀
安装:npm i postcss-loader autoprefixer -D
使用:webpack.config.js,module的rules中
{
test: /.css$/,
use: [
MinniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
'css-loader',
'postcss-loader',
]
},postcss.config.js中
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require("autoprefixer")({
overrideBrowserslist: ["last 2 versions", ">1%"]
})
]
};处理less
需要使用 less-loader,同时less-loader里面利用的是less故需安装less less-loader
安装:npm i less-loader less -D
使用:
{
test: /.less$/,
use: [
MinniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
'css-loader',
'postcss-loader',
'less-loader'
]
}sass同理
处理js
es6转es5
安装:npm i babel-loader @babel/core @babel/preset-env -D
使用:
{
test: /.js$/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
'@babel/preset-env'
],} } },</code></pre></div></div><h6 id="8rtq0" name="es7-%E8%BD%ACclass%E8%AF%AD%E6%B3%95"><strong>es7 转class语法</strong></h6><p>安装:<code>npm i @babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties -D</code></p><p>使用:</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">{ test: /\.js$/, use: { loader: 'babel-loader', options: { presets: [ '@babel/preset-env' ], plugins:[ ["@babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties", { "loose" : true }] ] } } },</code></pre></div></div><p>其他详细见babel官网</p><h4 id="3m4hj" name="1.2-%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%87"><strong>1.2 处理图片</strong></h4><p>一张图片的引用有三种方式</p><ul class="ul-level-0"><li>js中引入 创建图片标签引入</li><li>css引入 url</li><li>html中引入 img</li></ul><h5 id="dggc7" name="%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8file-loader"><strong>使用file-loader</strong></h5><p>第三张情况不可用,需要额外使用loader看下面栗子吧</p><p>安装:<code>npm i file-loader -D</code></p><p>本质就是引用是返回的是一张图片的地址,不过此张图片是已经在bundle中了</p><p>使用:<strong>「js中」</strong></p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">import './index.css'
import img from '../public/img/img01.jpg'
const image = new Image()
image.src = img
document.body.appendChild(image)
「css中」
div{
p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
transform: rotate(45deg);
background-image: url('./img01.jpg');
}
}「webpack.config.js中」
module.export={
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.(png|jpg|gif)$/,
use: 'file-loader'
}
]
}
}使用 url-loader
可当做file-loader的升级版,我们可以设置一张图片小于多少时使用base64,或者使用file-loader打包原图片
安装:npm i url-loader -D
同时这里可以使用html-withimg-loader处理html中的图片了,注意要把esModule属性设置为false。否则链如html中图片地址不对上面同理
安装:npm i html-withimg-loader -D
使用:
{
test: /.html$/,
use: 'html-withimg-loader'
}, {
test: /.(png|jpg|gif)$/,
use: {
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
limit: 50 * 1024,
loader: 'file-loader',
esModule: false,
outputPath: '/img/', // 打包后输出地址
// publicPath: '' // 给资源加上域名路径
}
}
},1.3 eslint
1.4 常用小插件
cleanWebpackPlugin
每次打包自动删除输出目录下的文件
安装:npm i clean-webpack-plugin -D
使用:
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
plugins:[
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
]
copyWebpackPlugin
可以一些没有依赖到,但是又需要输出倒dist下的文件
安装:npm i copy-webpack-plugin -D
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
plugins:[
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [{
from: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
to: 'dist'
}],
}),
]bannerPlugin
代码首部添加版权
webpack上的一个自带插件
使用:
const webpack = require('webpack')
plugins:[
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [{
from: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
to: 'dist'
}],
}),
new webpack.BannerPlugin('core by gxb'),
]
二:进价用法
2.1 多页面打包
即多入口,每个入口对应一个生成依赖树
配置很简单,配一下入口。入口格式为一个chunkNmae:path
entry: {
index: './src/index.js',
other: './src/other.js'
},
output: {
filename: '[name].js',
path: path.join(__dirname, './dist')
},
2.2 devtool :'source-map'
即源代码与打包后的代码之间的映射,就是在代码发生问题时可以通过source-map定位到原代码块
主要是在开发环境下使用
配置如下
devtool: 'source-map'devtool属性值有许多种,下面总结几个最常用的
- source-map 会产生映射.map文件,同时也能定位到行列
- cheap-module-source-map,不会产生.map文件,可定位到行【推荐配置】
- eval-source-map,不会产生.map文件,可定位行列
注意对于css、less、scss来说要想能定位到源码,还需在loader选项中进行配置
如:(请注意:笔者偷懒此段代码没有进行测试不知道现在过时没有)
test:/.css$,
use:[
'style-loader',
{
loader:'css-loader',
options:{
sourceMap:true
}
}
]2.3 watch
webpack中也可以配置watch监听器进行时时打包,即我们每次修改完代码之后不需要在自己输入命令了,直接c+s键保存即可。
配置如下:
module.exports = {
watch: true,
watchOptions: {
poll: 1000, // 每秒询问多少次
aggregateTimeout: 500, //防抖 多少毫秒后再次触发防止重复按键
ignored: /node_modules/ //忽略时时监听
}
}2.4 resolve
我们都清楚webpack启动之后会从入口文件开始寻找所有的依赖,但是像寻找一些第三方包的时候它总是会默认去找这个文件main.js为入口文件,但是像bootstrap我们有时候仅仅是需要引用它的样式。如果将它全部拿来打包,那么是不是有点太浪费了呢
resole在这里便可以指定webpack如何寻找模块对象的文件
配置如下:
resolve:{
modules:[path.join('node_modules')],//指定寻找目录
mainFields: ['style', 'main'],//优先用style没有则使用main
extensions: ['.js', '.css', '.json']//如果导入的文件没有后缀名,那么先看js文件有无,再看css...
alias:{
components: './src/components/'//增加别名,即使用import Button from 'components/button 导入时,实际上被 alias 等价替换成了 import Button from './src/components/button' 。
}
}其他选项请参考此文章
2.5 环境拆分
开发和线上的环境所需要配置的东西一般是不相同的,故可以利用webpack-merge,将配置文件拆分成一个基础公共、一个开发、一个线上的。
我们以后打包时就可以指定指定配置文件用于开发环境下打包或者产品环境下打包了。
安装:npm i webpack-merge -D
写法如下:
基础
const path = require('path')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: './src/index.html', filename: 'index.html' }), new CleanWebpackPlugin(), ], output: { filename: 'bundle.js', path: path.join(__dirname, './dist') },
}
开发:webpack.dev.js
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const common = require('./webpack.config')
module.exports = merge(base, {
mode: 'development',
devServer: {},
devtool: 'source-map'
})
线上:webpack.prod.js
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const common = require('./webpack.config.js');
module.exports = merge(common, {
mode: 'production',
});
2.6 处理跨域
笔者前面的文章总结过跨域,即利用代理处理跨域的思想就是:同源策略仅是存在于浏览器,服务器之间是不存在的。故我们可以先把数据发到一个代理服务器上
栗子:像一个不同域服务器发送请求
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('get', '/api/user', true);
xhr.send();
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
服务器代码:
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.get('/test', (req, res) => {
res.json({ msg: 11 })
})
app.listen(3001, function() {
console.log('启动服务');
})
webpack.config.js配置代理
devServer: {
port: 3000,
proxy: {
'/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:3001',
pathRewrite: { '^/api': '' }
}
},
progress: true,
contentBase: './dist',
open: true
},
三:优化
3.1 noparse
引用一些第三方包的时候,我们是不需要再进入这些包中再去寻找依赖,因为一般情况下均是独立的。
故不必再去解析浪费时间了
配置如下:
module: {
noParse: /jquery/, // 不用解析某些包的依赖
rules:[]
}3.2 include&exclude
同时我们也可以指定寻找的范围
如:
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
exclude: '/node_modules/', // 排除node_modules
include: path.resolve('src'), // 在src文件寻找
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
'@babel/preset-env',
]
}
}
}不建议使用exclude,要使用绝对路径
3.3 lgnorePlugin插件
有些第三方库中许多东西是我们用不到的,如一些有语言包的库。我们一般情况下是仅需要使用它里面的中文包的,其他各种语言包我们是不需要的。
故这是可以使webpack中提供的一个插件
const webpack = require('webpack')
plugins: [
new webpack.IgnorePlugin(/./locale/, /moment/)
]
3.4 多线程打包
使用插件happypack
安装:npm i happypack
使用:
const Happypack = require('happypack')
module:{
rules: [{
test: /.css$/,
use: 'happypack/loader?id=css'
}]
}
plugins:[
new Happypack({
id: 'css',
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader']
})
]
3.5 懒加载(按需加载)
即有些东西我们不用马上把它导入我们的依赖树中,而是用到它之后再导进来(就类似于按需加载)
这里需要@babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import用于 解析识别import()动态导入语法
安装:npm i @babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import -D
栗子:
index.js中:
const button = document.createElement('button')
button.innerHTML = '按钮'
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('click')
import ('./source.js').then(data => {
console.log(data.default)})
})
document.body.appendChild(button)
source.js
export default 'gxb'webpack.config.js
{
test: /.js$/,
include: path.resolve('src'),
use: [{
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
'@babel/preset-env',
],
plugins: [
'@babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import'
]
}
}]
}即source.js模块仅仅当我们点击了按钮之后才会加入依赖,否则不会立即打包
3.6 热更新
即代码更新是页面只会更新该更新的地方而不是重新渲染整个页面,即重新刷新页面
热更新插件也是webpack上自带的
配置如下:
devServer: {
hot: true,
port: 3000,
contentBase: './dist',
open: true
},
plugins:[
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin()
]
3.7 DllPlugin动态链接库
我们使用vue或react时,每次打包文件均需要把他们打一遍。但是这种第三方包大不说,它内部在我们编译时根本也不会发生变化。
那么我们将它们在第一次打包时打出来,然后链接到我们的文件中不好吗
这些提前打包好文件名叫做dll,其实就可以理解成一个缓存
怎样写一个缓存呢?思路可能是这样的
- 先把东西存起来
- 搞一个映射表,后面要用到时先查映射表中的东西,有则直接用
但是这玩意配置还是挺麻烦的,但是有个好消息。dll已经被废弃掉了
再但是既然写了这个标题还是搞一下作为了解吧
直接使用插件 autodll-webpack-plugin
安装npm i autodll-webpack-plugin
使用:
const path = require('path');
const AutoDllPlugin = require('autodll-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
// 配置要打包为 dll 的文件
new AutoDllPlugin({
inject: true, // 设为 true即 DLL bundles 插到 index.html 里
filename: '[name].dll.js',
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'), // AutoDllPlugin 的 context 必须和 package.json 的同级目录,要不然会链接失败
entry: {
react: [
'react',
'react-dom'
]
}
})
]
}
Dll之后的可以使用 HardSourceWebpackPlugin,比dll更快更简单
安装:npm i hard-source-webpack-plugin
使用
const HardSourceWebpackPlugin = require('hard-source-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HardSourceWebpackPlugin()
]
}
3.8 抽取公共代码
尤其是在一些多入口文件中,如入口index.js引用了a.js,又一个入口的other.js又引用了a.js,那么正常情况下a.js会被打印两次。嗯。。那可是没有必要的
抽取:
module.exports = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: { // 分割代码块,针对多入口
cacheGroups: { // 缓存组
common: { // 公共模块
minSize: 0, // 大于0k抽离
minChunks: 2, // 被引用多少次以上抽离抽离
chunks: 'initial' // 从什么地方开始, 从入口开始
}
}
}
},
}抽取一些像jquery这样的一般被多次引用的第三方包
optimization: {
splitChunks: { // 分割代码块,针对多入口
cacheGroups: { // 缓存组
common: { // 公共模块
minSize: 0, // 大于多少抽离
minChunks: 2, // 使用多少次以上抽离抽离
chunks: 'initial' // 从什么地方开始,刚开始
},
vendor: {
priority: 1, // 增加权重, (先抽离第三方)
test: /node_modules/, // 把此目录下的抽离
minSize: 0, // 大于多少抽离
minChunks: 2, // 使用多少次以上抽离抽离
chunks: 'initial' // 从什么地方开始,刚开始
}
}
},
},3.8 webpack内置一些优化
自动了解吧,这里面没有啥东西

四:tapable ——手写早知道
tapable是一个类似于nodejs的eventEmitter的库,主要功能是控制各种钩子函数的发布与订阅,控制着webpack的插件系统
4.1 同步
4.1.1 SyncHook的用法与实现
最没有特点的一个hook,就是同步串行
const { SyncHook } = require('tapable')class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
arch: new SyncHook(['name']),
}
}
start() {
this.hooks.arch.call('gxb')
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tap('node', function(name) {
console.log('node', name)
})
this.hooks.arch.tap('react', function(name) {
console.log('react', name)
})
}
}const l = new Lesson()
l.tap();
l.start()
// 实现
class SyncHook {
constructor() {
this.tasks = []
}
tap(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
call(...arg) {
this.tasks.forEach(item => {
item.cb(...arg)
})
}
}
const syncHook = new SyncHook()
syncHook.tap('node', name => {
console.log('node', name)
})
syncHook.tap('vue', name => {
console.log('vue', name)
})
syncHook.call('gxb')
4.1.2 SyncBailHook的用法与实现
/**
- 订阅的处理函数有一个的返回值不是undefined就停止向下跑
*/
const { SyncBailHook } = require('tapable')class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
arch: new SyncBailHook(['name'])
}
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tap('node', (name) => {
console.log('node', name);
return 'error'
})
this.hooks.arch.tap('vue', (name) => {
console.log('vue', name);
return undefined
})
}
start() {
this.hooks.arch.call('gxb')
}}
const l = new Lesson()
l.tap()
l.start()/**
- 方法实现
*/
class SyncBailHook {
//一般是可以接收一个数组参数的,但是下面没有用到
constructor(args) {
this.tasks = []
}
tap(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
call(...arg) {
let ret
let index = 0
do {
ret = this.tasks[index++].cb(...arg)
} while (ret === undefined && index < this.tasks.length);
}
}const syncBailHook = new SyncBailHook()
syncBailHook.tap('node', name => {
console.log('node', name);
return 'error'
})
syncBailHook.tap('vue', name => {
console.log('vue', name);
})
syncBailHook.call('gxb')
4.1.3 SyncWaterfallHook的用法与与实现
/**
- 上一个处理函数的返回值是下一个的输入
/
/*- 订阅的处理函数有一个的返回值不是undefined就停止向下跑
*/
const { SyncWaterfallHook } = require('tapable')class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
arch: new SyncWaterfallHook(['name'])
}
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tap('node', (name) => {
console.log('node', name);
return 'node ok'
})
this.hooks.arch.tap('vue', (data) => {
console.log('vue', data);}) } start() { this.hooks.arch.call('gxb') }}
const l = new Lesson()
l.tap()
l.start()/**
- 方法实现
*/
class SyncWaterfallHook {
//一般是可以接收一个数组参数的,但是下面没有用到
constructor(args) {
this.tasks = []
}
tap(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
call(...arg) {
let [first, ...others] = this.tasks
let ret = first.cb(...arg)
others.reduce((pre, next) => {
return next.cb(pre)
}, ret)
}
}const syncWaterfallHook = new SyncWaterfallHook()
syncWaterfallHook.tap('node', data => {
console.log('node', data);
return 'error'
})
syncWaterfallHook.tap('vue', data => {
console.log('vue', data);
})
syncBailHook.call('gxb')
4.1.4 SyncLoopHook的用法与实现
/**
- 订阅的处理函数有一个的返回值不是undefined就一直循环它
*/
const { SyncLoopHook } = require('tapable')class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.index = 0
this.hooks = {
arch: new SyncLoopHook(['name'])
}
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tap('node', (name) => {
console.log('node', name);
return ++this.index === 3 ? undefined : this.index
})
this.hooks.arch.tap('vue', (name) => {
console.log('vue', name);
return undefined
})
}
start() {
this.hooks.arch.call('gxb')
}}
const l = new Lesson()
l.tap()
l.start()/**
- 方法实现
*/
class SyncLoopHook {
//一般是可以接收一个数组参数的,但是下面没有用到
constructor(args) {
this.tasks = []
}
tap(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
call(...arg) {
this.tasks.forEach(item => {
let ret;
do {
ret = item.cb(...arg)
} while (ret !== undefined);
})
}
}const syncLoopHook = new SyncLoopHook()
let index = 0
syncLoopHook.tap('node', name => {
console.log('node', name);
return ++index === 3 ? undefined : index
})
syncLoopHook.tap('vue', name => {
console.log('vue', name);
})
syncLoopHook.call('gxb')
4.2 异步
异步并发
4.2.1 AsyncParallelHook
/**
-
异步并发,
串行与并发的关系
即并发需要把处理函数全部执行完再走最后的回调,而串行是一个处理函数执行完才走第二个
*/
const { AsyncParallelHook } = require("tapable")
class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
arch: new AsyncParallelHook(['name'])
}
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tapAsync('node', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("node", name);
cb();
}, 1000);
})
this.hooks.arch.tapAsync('vue', (name, cb) => {
// 使用宏任务
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('vue', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
}
start() {
this.hooks.arch.callAsync('gxb', function() {
console.log('end')
})
}
}
let l = new Lesson();
l.tap();
l.start();
/**
-
实现
-
异步并发回忆特点,callAsync传入的回调是在所有异步任务执行完成之后执行的
*/
class SyncParralleHook {
constructor() {
this.tasks = []
}
tapAsync(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
//主要就是每一个异步处理函数执行完都在跑一下done,看是否该执行最后的回调了吗
callAsync(...arg) {
// 先拿出callAsync传过来的回调
const lastCb = arg.pop()
// 开始执行其他的异步任务
let index = 0
// done函数用来判断是不是要去执行lastCb了
const done = () => {
//根据异步函数的数量来执行lastCb
index++
if (index === this.tasks.length) {
lastCb()
}
}
this.tasks.forEach(item => item.cb(...arg, done))
}
}
const hook = new SyncParralleHook()
hook.tapAsync('node', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('node', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
hook.tapAsync('vue', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('vue', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
hook.callAsync('gxb', function() {
console.log('end')
})
/**
- 处理函数是用微任务promis,即处理函数可以不传回调cb但是需要返回一个promise
*/
const { AsyncParallelHook } = require('tapable')
class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
arch: new AsyncParallelHook(['name'])
}
}
start() {
this.hooks.arch.promise('gxb').then(function() {
console.log('end')
})
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tapPromise('node', name => {
return new Promise((resove, reject) => {
console.log('node', name)
resove()
})
})
this.hooks.arch.tapPromise('vue', name => {
return new Promise((resove, reject) => {
console.log('vue', name)
resove()
})
})
}
}
const l = new Lesson()
l.tap()
l.start()
/**
- 实现
- tapPromise
promise
/
class AsyncParallelHook {
constructor() {
this.tasks = []
}
tapPromise(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
promise(...arg) {
// task中的处理函数部分返回值都是promise,将它们映射一个数组中。使用promise的all全部执行他们
const newTasks = this.tasks.map(item => item.cb(...arg))
return Promise.all(newTasks)
}
}
// 测试
const hook = new AsyncParallelHook()
hook.tapPromise('node', name => {
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
console.log('node', name)
res()
})
})
hook.tapPromise('vue', name => {
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
console.log('vue', name)
res()
})
})
hook.promise('gxb').then(function() {
console.log('end')
})
4.2.2AsyncParallelBailHook
和同步同理
异步串行
4.2.3 AsyncSeriesHook
/*异步串行 一个by一个的执行 */
const { AsyncSeriesHook } = require('tapable')
class Lesson {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
arch: new AsyncSeriesHook(['name'])
}
}
start() {
this.hooks.arch.callAsync('gxb', function() {
console.log('end')
})
}
tap() {
this.hooks.arch.tapAsync('node', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('node', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
this.hooks.arch.tapAsync('vue', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('node', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
}
}
const l = new Lesson()
l.tap()
l.start()/**
实现
特点:一个函数执行完再执行再一个
*/
class AsyncSeriesHook {
constructor() {
this.tasks = []
}
tapAsync(name, cb) {
let obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.cb = cb
this.tasks.push(obj)
}
callAsync(...arg) {
const finalCb = arg.pop()
let index = 0
let next = () => {
if (this.tasks.length === index) return finalCb()let task = this.tasks[index++].cb task(...arg, next) } next()}
}
const hook = new AsyncSeriesHook()
hook.tapAsync('node', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('node', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
hook.tapAsync('vue', (name, cb) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('vue', name)
cb()
}, 1000)
})
hook.callAsync('gxb', function() {
console.log('end')
})
4.2.4 AsyncSeriesBailHook
参考同步
4.2.5 AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
参考同步

五:手写一个简单的webpack
5.1 构建入口文件,即link到本地
初始化一个新的项目,首先npm init -y生成package.json
写一个bin命令
"bin": {
"mypack": "./bin/index.js"
},./bin/index.js作为我们的入口文件
再运行npm link, 将npm 模块链接到对应的运行项目中去,方便地对模块进行调试和测试
再创建一个写了webpack.config.js文件的项目(先称之为要打包的项目文件吧——>源码项目)。运行命令`npm link mypack
这是在要打包的项目中运行命令 npx mypack,其所用的就是我们手写的那个了
5.2 构建核心,compiler类的编写
回到手写webpack项目下初始化compiler类
入口文件中没什么东西
只是需要拿到源码项目下的webpack.config.js,接下来调用compiler方法将拿到的配置文件地址传进去
#! /usr/bin/env nodeconst path = require('path')
// 拿配置文件
const config = require(path.resolve('webpack.config.js'))
const Compiler = require('../lib/compiler.js')
const compiler = new Compiler(config)
compiler.run()
Compiler类的基本骨架
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const tapable = require('tapable')
class Compiler {
constructor(config) {
this.config = config
this.entryId = ''
this.modules = {}
this.entry = config.entry
this.root = process.cwd() //拿到当前项目地址
this.asserts = {} // 存储chunkName与输出代码块
this.hooks = {
entryInit: new tapable.SyncHook(),
beforeCompile: new tapable.SyncHook(),
afterCompile: new tapable.SyncHook(),
afterPlugins: new tapable.SyncHook(),
afteremit: new tapable.SyncHook(),
}const plugins = this.config.plugins if (Array.isArray(plugins)) { plugins.forEach(item => { // 每个均是实例,调用实例上的一个方法即可,传入当前Compiler实例 item.run(this) }) } } // 构建模块 buildMoudle(modulePath, isEntry) {} //写的输出位置 emitFile() {} run() { this.hooks.entryInit.call() this.buildMoudle(path.resolve(this.root, this.entry), true) this.hooks.afterCompile.call() this.emitFile() }
}
构建模板
首先run中传过来的是一个入口地址,和一个标志是不是入口的布尔。我们要做的是首先入口的相对地址赋值给this.entryId
然后获取文件源码,搞成{文件相对地址:改造后源码}这种键值对的形式
// 构建模块
buildMoudle(modulePath, isEntry) {
let source = this.getSource(modulePath)// 其实就是this.entry 啊 let moduleName = './' + path.relative(this.root, modulePath) if (isEntry) { this.entryId = moduleName } // 开始改造源码,主要针对require let { sourceCode, dependencies } = this.parse(source, path.dirname(moduleName)) //就是./src // 改造完成放入模块中 this.modules[moduleName] = sourceCode // 递归构造依赖模板 dependencies.forEach(item => { this.buildMoudle(path.resolve(this.root, item), false) }) }</code></pre></div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0"> // 获取源码 getSource(modulePath) { // 事先拿module中的匹配规则与路径进行匹配 let content = fs.readFileSync(modulePath, 'utf8') return content }</code></pre></div></div><p>改造源码</p><p>这里要用到一些工具</p><ul class="ul-level-0"><li><code>babylon</code> 将源码搞成AST抽象语法树</li><li><code>@babel/traverse</code>用于替换AST上的节点</li><li><code>@babel/generator</code> 结果生成</li><li><code>@babel/types</code> AST节点的Lodash-esque实用程序库</li></ul><p>安装:<code>npm i babylon @babel/traverse @babel/types @babel/generator</code></p><p>源码:就是将require换成<code>__webpack_require__</code>,同时在改造一下require的内部路径参数。其实webpack可是打包require本质就是手动实现了一个require方法</p><p>注意:本次只是重写了require,可仍是不支持es6模块的啊</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">// 源码改造 parse(source, parentPath) { // 生成ast语法树 let ast = babylon.parse(source) // 用于存取依赖 let dependencies = [] traverse(ast, { CallExpression(p) { let node = p.node // 对require方法进行改名 if (node.callee.name === 'require') { node.callee.name = '__webpack_require__' let moduledName = node.arguments[0].value // 取到require方法里的路径 // 改造其后缀名 moduledName = moduledName + (path.extname(moduledName) ? '' : '.js') // 加上其父路径./src moduledName = './' + path.join(parentPath, moduledName) // 加入依赖数组 dependencies.push(moduledName) // 源码替换 node.arguments = [type.stringLiteral(moduledName)] } } }) let sourceCode = generator(ast).code return { sourceCode, dependencies } }</code></pre></div></div><h5 id="pgqm" name="%E8%BE%93%E5%87%BA%E5%88%B0output%E7%9A%84%E6%8C%87%E5%AE%9A%E4%BD%8D%E7%BD%AE"><strong>输出到output的指定位置</strong></h5><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">//写到输出位置 emitFile() { // 拿到输出地址 let outPath = path.join(this.config.output.path, this.config.output.filename) // 拿模板 let templateStr = this.getSource(path.join(__dirname, 'main.ejs')) // 填充模板数据 let code = ejs.render(templateStr, { entryId: this.entryId, modules: this.modules }) this.asserts[outPath] = code console.log(code); // 写入 fs.writeFileSync(outPath, this.asserts[outPath]) }
(function (modules) {
var installedModules = {};function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { if (installedModules[moduleId]) { return installedModules[moduleId].exports; } var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} }; modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); module.l = true; return module.exports; } // Load entry module and return exports return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "<%-entryId %>"); })({ <% for(let key in modules){ %> "<%- key %>": (function (module, exports,__webpack_require__) { eval(`<%-modules[key] %>`); }), <% } %> });</code></pre></div></div><h5 id="al67h" name="%E5%8A%A0%E5%85%A5loader"><strong>加入<code>loader</code></strong></h5><p>写一个less-loader和style-loader,css-loader只是处理一些css中的@import的语法,故这里为求简便不写css-loader了</p><p>less-loader:注要就是借用less,将less文件转为css文件</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">const less = require('less')function loader(source) {
let css = ''
less.render(source, function(err, output) {
css = output.css
})css = css.replace(/\n/g, '\\n') return css
}
module.exports = loader
style-loader:搞一个标签,将css放进去
function loader(source) {
let style = let style = document.createElement('style') style.innerHTML = ${JSON.stringify(source)} document.head.appendChild(style)
return style
}
module.exports = loader此时的webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.join(__dirname, './dist')
},
module: {
rules: [{
test: /.less$/,
use: [path.join(__dirname, './loader/style-loader.js'), path.join(__dirname, './loader/less-loader.js')]
}]
},
plugins: [
new TestPlugins(),
new InitPlugin()
]
}此时源码文件获取函数改造如下
// 获取源码
getSource(modulePath) {
// 事先拿module中的匹配规则与路径进行匹配
const rules = this.config.module.rules
let content = fs.readFileSync(modulePath, 'utf8')for (let i = 0; i < rules.length; i++) { let { test, use } = rules[i] let len = use.length // 匹配到了开始走loader,特点从后往前 if (test.test(modulePath)) { console.log(111); function normalLoader() { // 先拿最后一个 let loader = require(use[--len]) content = loader(content) if (len > 0) { normalLoader() } } normalLoader() } } return content }</code></pre></div></div><h5 id="a0fpa" name="%E5%B9%B6%E6%B7%BB%E5%8A%A0%E6%8F%92%E4%BB%B6"><strong>并添加插件</strong></h5><p>直接在源码项目的webpack.config.js中编写吧</p><div class="rno-markdown-code"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-info"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-item is-type"><span class="is-m-hidden">代码语言:</span>javascript</div></div><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-opt"><div class="rno-markdown-code-toolbar-copy"><i class="icon-copy"></i><span class="is-m-hidden">复制</span></div></div></div><div class="developer-code-block"><pre class="prism-token token line-numbers language-javascript"><code class="language-javascript" style="margin-left:0">const path = require('path')class TestPlugins {
run(compiler) {
// 将自身方法订阅到hook以备使用
//假设它的运行期在编译完成之后
compiler.hooks.afterCompile.tap('TestPlugins', function() {
console.log(this is TestPlugins,runtime ->afterCompile);}) }}
class InitPlugin {
run(compiler) {
// 将的在执行期放到刚开始解析入口前
compiler.hooks.entryInit.tap('Init', function() {
console.log(this is InitPlugin,runtime ->entryInit);
})
}
}
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.join(__dirname, './dist')
},
module: {
rules: [{
test: /.less$/,
use: [path.join(__dirname, './loader/style-loader.js'), path.join(__dirname, './loader/less-loader.js')]
}]
},
plugins: [
new TestPlugins(),
new InitPlugin()
]
}
其实手写逻辑还是比较难说清楚的,还不如直接看代码,下面我将compiler类的全部代码粘了出来,其中注释已经写得自我感觉很详细了
compiler类全部代码
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const { assert } = require('console')
// babylon 主要把源码转成ast Babylon 是 Babel 中使用的 JavaScript 解析器。
// @babel/traverse 对ast解析遍历语法树 负责替换,删除和添加节点
// @babel/types 用于AST节点的Lodash-esque实用程序库
// @babel/generator 结果生成
const babylon = require('babylon')
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default;
const type = require('@babel/types');
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default
const ejs = require('ejs')
const tapable = require('tapable')
class Compiler {
constructor(config) {
this.config = config
this.entryId = ''
this.modules = {}
this.entry = config.entry
this.root = process.cwd() //当前项目地址
this.asserts = {} // 存储chunkName与输出代码块
this.hooks = {
entryInit: new tapable.SyncHook(),
beforeCompile: new tapable.SyncHook(),
afterCompile: new tapable.SyncHook(),
afterPlugins: new tapable.SyncHook(),
afteremit: new tapable.SyncHook(),
}
const plugins = this.config.plugins
if (Array.isArray(plugins)) {
plugins.forEach(item => {
// 每个均是实例,调用实例上的一个方法即可,传入当前Compiler实例
item.run(this)
})
}
}
// 获取源码
getSource(modulePath) {
// 事先拿module中的匹配规则与路径进行匹配
const rules = this.config.module.rules
let content = fs.readFileSync(modulePath, 'utf8')
for (let i = 0; i < rules.length; i++) {
let { test, use } = rules[i]
let len = use.length
// 匹配到了开始走loader,特点从后往前
if (test.test(modulePath)) {
console.log(111);
function normalLoader() {
// 先拿最后一个
let loader = require(use[--len])
content = loader(content)
if (len > 0) {
normalLoader()
}
}
normalLoader()
}
}
return content
}
// 源码改造
parse(source, parentPath) {
// ast语法树
let ast = babylon.parse(source)
// 用于存取依赖
let dependencies = []
traverse(ast, {
CallExpression(p) {
let node = p.node
// 对require方法进行改名
if (node.callee.name === 'require') {
node.callee.name = '__webpack_require__'
let moduledName = node.arguments[0].value // 取到require方法里的路径
// 改造其后缀名
moduledName = moduledName + (path.extname(moduledName) ? '' : '.js')
// 加上其父路径./src
moduledName = './' + path.join(parentPath, moduledName)
// 加入依赖数组
dependencies.push(moduledName)
// 源码替换
node.arguments = [type.stringLiteral(moduledName)]
}
}
})
let sourceCode = generator(ast).code
return { sourceCode, dependencies }
}
// 构建模块
buildMoudle(modulePath, isEntry) {
let source = this.getSource(modulePath)
// 其实就是this.entry 啊
let moduleName = './' + path.relative(this.root, modulePath)
if (isEntry) {
this.entryId = moduleName
}
// 开始改造源码,主要针对require
let { sourceCode, dependencies } = this.parse(source, path.dirname(moduleName)) //就是./src
// 改造完成放入模块中
this.modules[moduleName] = sourceCode
// 递归构造依赖模板
dependencies.forEach(item => {
this.buildMoudle(path.resolve(this.root, item), false)
})
}
//写的输出位置
emitFile() {
// 拿到输出地址
let outPath = path.join(this.config.output.path, this.config.output.filename)
// 拿模板
let templateStr = this.getSource(path.join(__dirname, 'main.ejs'))
// 填充模板数据
let code = ejs.render(templateStr, {
entryId: this.entryId,
modules: this.modules
})
this.asserts[outPath] = code
console.log(code);
// 写入
fs.writeFileSync(outPath, this.asserts[outPath])
}
run() {
this.hooks.entryInit.call()
this.buildMoudle(path.resolve(this.root, this.entry), true)
this.hooks.afterCompile.call()
this.emitFile()
}
}
module.exports = Compiler
/**
到此为止一个简单的webpack就已经完成了
*/
写到最后,到了这里webpack应该算是正式入了门。下面的东西留到以后总结吧。脑图就不上传了哈
参考致谢:
webpack系列之二Tapable
轻松通过两个实例来理解 webpack 中的 devtool: 'source-map' 是什么意思
这才是官方的tapable中文文档
npm link用法总结
如何开发webpack loader
玩转webpack
搞定webpack4
webpack实战:入门、进阶与调优