01、前言
在本项目中,我们将使用MetPy库来计算准地转Omega方程中涡度平流项和温度平流的拉普拉斯算子。根据Bluesetein(1992;Eq.5.6.11)提出的QG-Omega方程,我们将关注方程右侧的两个主要强迫项
QG-Omega方程描述了大气垂直运动速度(Omega)与静力力作用(QG项)之间的关系。通过计算微分涡度平流项和温度平流的拉普拉斯算子,并将它们在700百帕时进行有效性验证,我们将深入研究大气垂直运动的演变过程,从而更好地理解大气运动规律和预测能力。
在编写代码时,我们需要设置静态稳定度、f0和Rd的常数,并结合MetPy库提供的功能来进行数值计算。通过对这些项的计算,我们将得到在特定压力层(例如700百帕)上的结果,从而为QG-Omega方程的研究提供实质性的数值支持。
本质上,准地转(QG)ω方程能够通过检查同期天气图来获得主要天气尺度上升区域的定性指示。此外,它允许在给定三维地转流场规范的情况下计算垂直速度场的一阶定量估计。其诊断价值的一个迹象是,强烈的低层上升可以促进气旋形成,有利于降水的发生。 Davies, H. C., 2015: The Quasigeostrophic Omega Equation: Reappraisal, Refinements, and Relevance. Mon. Wea. Rev., 143, 3–25, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-14-00098.1
⑴ 温度平流,单位K•s-1;量级为10-5
温度的冷暖平流是表明大气斜压性的一种度量,大尺度天气系统的发生发展均与之有关。此外预报还常关注850hPa和500hPa温度平流的差值,若差值>0,则表明低层有暖平流,高层为冷平流,有利于不稳定层结加强,反之,则表明低层有冷平流,高层为暖平流,不利于不稳定层结的加强。
⑵ 涡度平流,单位:s-2;量级为10-10
表征由水平风引起的涡度输送,其中相对涡度平流的作用是使槽脊移动。高空槽前的正涡度平流可引起辐散,槽后的负涡度平流可引起辐合。
http://stream1.cmatc.cn/cmatcvod/12/tqx/second_content.html
02、温馨提示
完整代码在项目地址#小程序://和鲸社区/UEwXbrO96nV6puE
由于可视化代码过长隐藏,可点击运行查看
🔜🔜若没有成功加载可视化图,点击运行可以查看
ps:隐藏代码在【代码已被隐藏】所在行,点击所在行,可以看到该行的最右角,会出现个三角形,点击查看即可
03、导入库与读取文件
from datetime import datetimeimport cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
import numpy as np
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import metpy.calc as mpcalc
import metpy.constants as mpconstants
from metpy.units import units
import xarray as xr
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom netCDF4 import Dataset
from wrf import getvar, ALL_TIMES,interplevelIn [3]:
定义 WRF 文件夹路径和文件名前缀
wrfout_path = "/home/mw/input/typhoon9537"
filename_prefix = "wrfout_d01_"获取 WRF 文件列表,并按照文件名排序
wrf_files = sorted([os.path.join(wrfout_path, f) for f in os.listdir(wrfout_path) if f.startswith(filename_prefix)])
wrf_list = [Dataset(f) for f in wrf_files]提取变量
lons = getvar(wrf_list[0], 'lon', timeidx=0)
lats = getvar(wrf_list[0], 'lat', timeidx=0)
04读取变量
dx, dy = mpcalc.lat_lon_grid_deltas(lons, lats)
z = getvar(wrf_list[5], 'z', units="m", timeidx=0)
u = getvar(wrf_list[5], 'ua', timeidx=0)
v = getvar(wrf_list[5], 'va', timeidx=0)
t = getvar(wrf_list[5], 'tc', timeidx=0)
p = getvar(wrf_list[5], 'pressure', timeidx=0)
z700 = interplevel(z, p, 700)
t700 = interplevel(t, p, 700)
u700 = interplevel(u, p, 700)
v700 = interplevel(v, p, 700)
t500 = interplevel(t, p, 500)
z500 = interplevel(z, p, 500)
u900 = interplevel(u, p, 900)
v900 = interplevel(v, p, 900)
u500 = interplevel(u, p, 500)
v500 = interplevel(v, p, 500)
sigma = 2.0e-6 * units('m^2 Pa^-2 s^-2')
f0 = 1e-4 * units('s^-1')
Rd = mpconstants.Rd05、计算Term A -涡度平流项
# 绝对涡度平流
avo = getvar(wrf_list[0], 'avo', timeidx=0)
avor_900 = interplevel(z, p, 900) * units('1/s') *10**-5
avor_500 = interplevel(z, p, 500) * units('1/s') *10**-5vortadv_900 = mpcalc.advection(avor_900, u900, v900, dx=dx, dy=dy)
vortadv_500 = mpcalc.advection(avor_500, u500, v500, dx=dx, dy=dy)两层绝对涡度平流差分
diff_avor = ((vortadv_900 - vortadv_500)/(400 * units.hPa))
Calculation of final differential vorticity advection term
term_A = (-f0 / sigma * diff_avor)
06、计算 Term B - 温度平流的拉普拉斯项
# 700-hPa Temperature Advection
tadv_700 = mpcalc.advection(t700, u700, v700, dx=dx, dy=dy)Laplacian of Temperature Advection
lap_tadv_700 = mpcalc.laplacian(tadv_700, deltas=(dy, dx))
Final term B calculation with constants
term_B = (-Rd / (sigma * (700 * units.hPa)) * lap_tadv_700)
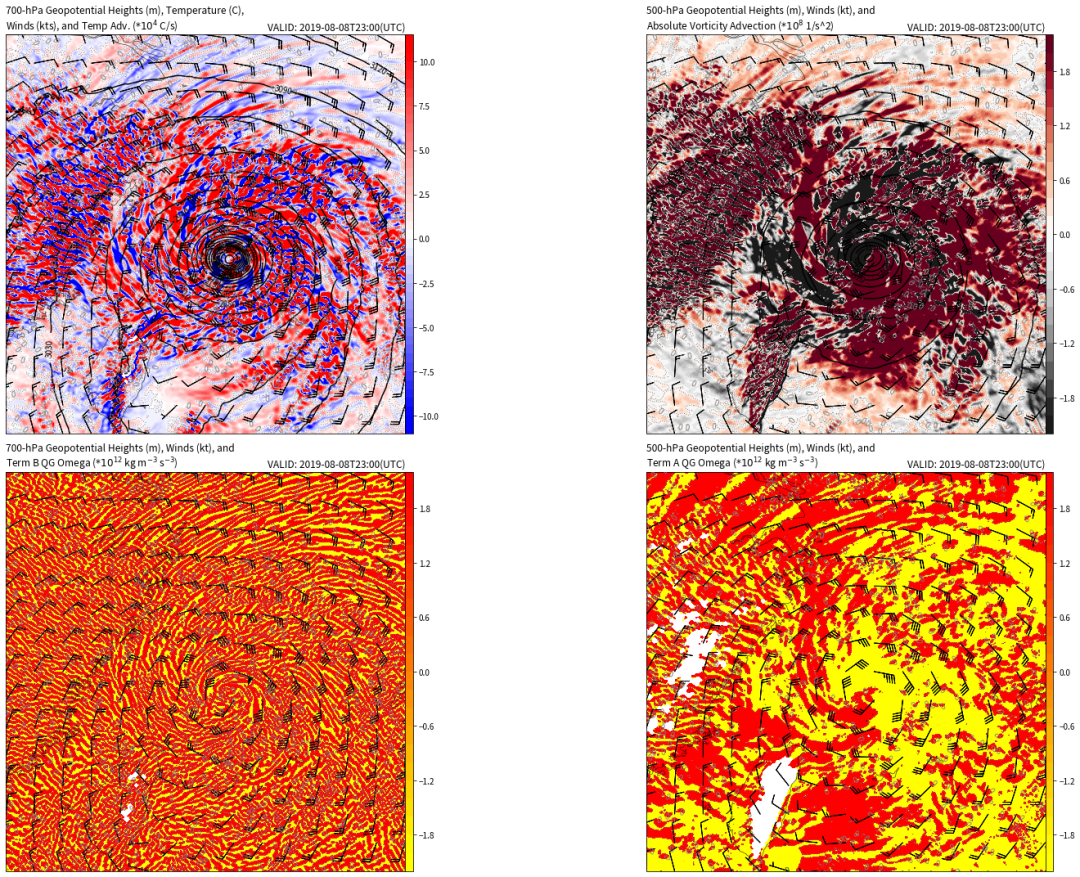
07、绘图
左上:700百帕的位势高度、温度和风
右上:500百帕位势高度、绝对涡度和风
左下:tremB(温度平流的拉普拉斯项)
右下:termA(涡度平流的拉普拉斯项)
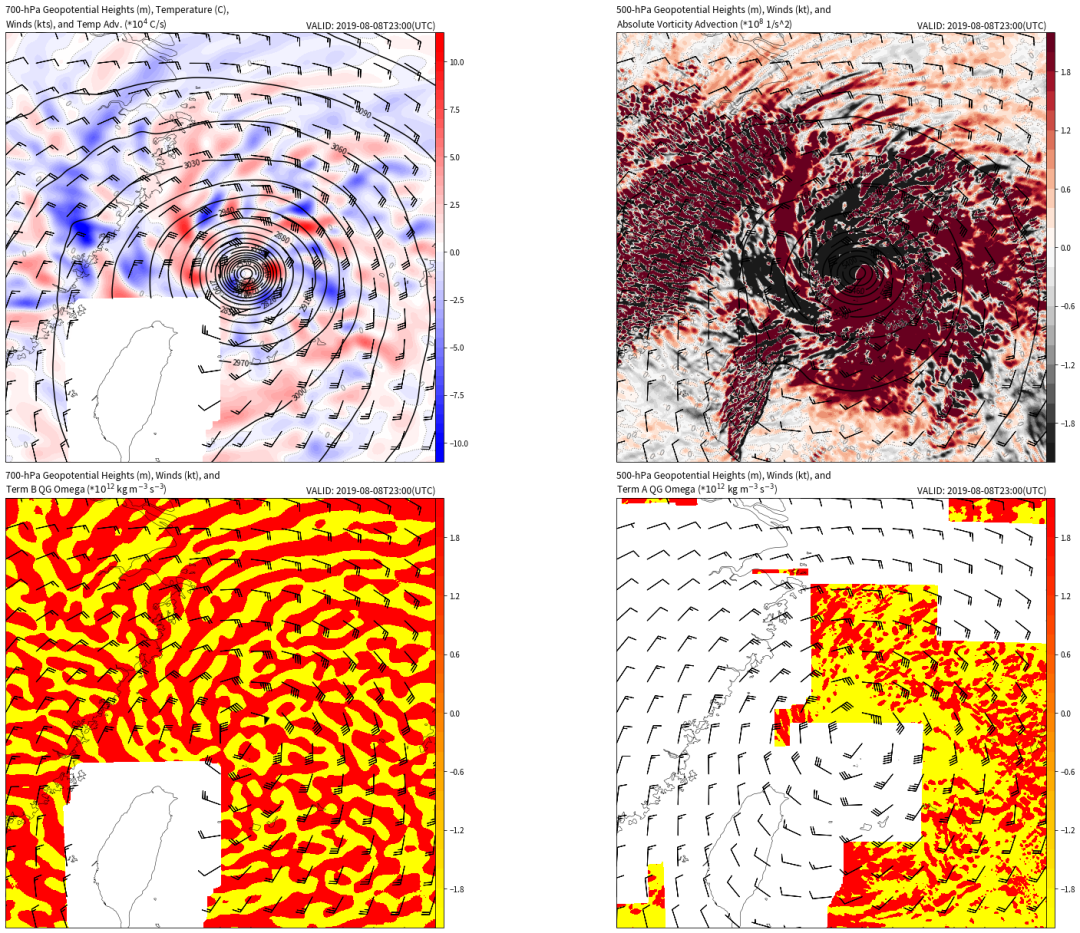
08、九点平滑30次后绘图
n_reps = 50Apply the 9-point smoother
z700s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(z700, 9, n_reps)
z500s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(z500, 9, n_reps)t700s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(t700, 9, n_reps)
t500s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(t500, 9, n_reps)u700s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(u700, 9, n_reps)
v700s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(v700, 9, n_reps)u500s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(u500, 9, n_reps)
v500s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(v500, 9, n_reps)
u900s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(u900, 9, n_reps)
v900s = mpcalc.smooth_n_point(v900, 9, n_reps)
09、绘制右侧项总和(未平
In [27]:
combined_terms = term_A + term_Bplt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.set_extent([118, 128, 22, 32], ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.add_feature(cfeature.COASTLINE, linewidth=0.5)cf = ax.contourf(lons, lats, combined_terms,
cmap='autumn_r', extend='both', transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
plt.colorbar(cf, orientation='horizontal', pad=0.05, aspect=40, extendrect=True)
plt.title('Combined QG Omega Forcing Terms')
plt.show()
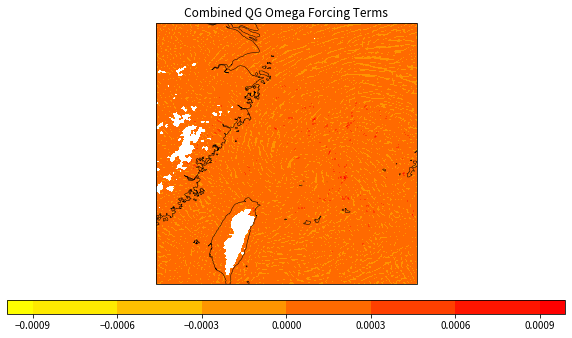
当然台风的天气形势是相对极端的,计算出的量级较大
如果以上计算有错,还请指正,谢谢大家